Low-dose irradiation affects expression of inflammatory markers in the heart of ApoE -/- mice
- PMID: 25799423
- PMCID: PMC4370602
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119661
Low-dose irradiation affects expression of inflammatory markers in the heart of ApoE -/- mice
Erratum in
-
Correction: Low-Dose Irradiation Affects Expression of Inflammatory Markers in the Heart of ApoE -/- Mice.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 9;11(6):e0157616. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157616. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27280530 Free PMC article.
Abstract
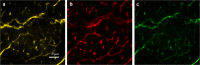
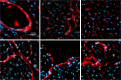
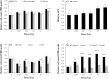
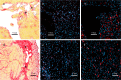
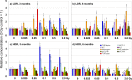
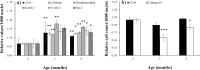
Epidemiological studies indicate long-term risks of ionizing radiation on the heart, even at moderate doses. In this study, we investigated the inflammatory, thrombotic and fibrotic late responses of the heart after low-dose irradiation (IR) with specific emphasize on the dose rate. Hypercholesterolemic ApoE-deficient mice were sacrificed 3 and 6 months after total body irradiation (TBI) with 0.025, 0.05, 0.1, 0.5 or 2 Gy at low (1 mGy/min) or high dose rate (150 mGy/min). The expression of inflammatory and thrombotic markers was quantified in frozen heart sections (CD31, E-selectin, thrombomodulin, ICAM-1, VCAM-1, collagen IV, Thy-1, and CD45) and in plasma samples (IL6, KC, MCP-1, TNFα, INFγ, IL-1β, TGFβ, INFγ, IL-10, sICAM-1, sE-selectin, sVCAM-1 and fibrinogen) by fluorescence analysis and ELISA. We found that even very low irradiation doses induced adaptive late responses, such as increases of capillary density and changes in collagen IV and Thy-1 levels indicating compensatory regulation. Slight decreases of ICAM-1 levels and reduction of Thy 1 expression at 0.025-0.5 Gy indicate anti-inflammatory effects, whereas at the highest dose (2 Gy) increased VCAM-1 levels on the endocardium may represent a switch to a pro-inflammatory response. Plasma samples partially confirmed this pattern, showing a decrease of proinflammatory markers (sVCAM, sICAM) at 0.025-2.0 Gy. In contrast, an enhancement of MCP-1, TNFα and fibrinogen at 0.05-2.0 Gy indicated a proinflammatory and prothrombotic systemic response. Multivariate analysis also revealed significant age-dependent increases (KC, MCP-1, fibrinogen) and decreases (sICAM, sVCAM, sE-selectin) of plasma markers. This paper represents local and systemic effects of low-dose irradiation, including also age- and dose rate-dependent responses in the ApoE-/- mouse model. These insights in the multiple inflammatory/thrombotic effects caused by low-dose irradiation might facilitate an individual evaluation and intervention of radiation related, long-term side effects but also give important implications for low dose anti-inflammatory radiotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Takahashi I, Abbott RD, Ohshita T, Takahashi T, Ozasa K, Akahoshi M, et al. A prospective follow-up study of the association of radiation exposure with fatal and non-fatal stroke among atomic bomb survivors in Hiroshima and Nagasaki (1980–2003). BMJ Open 2012;2: e000654 10.1136/bmjopen-2011-000654 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jurcut R, Savu O, Giusca S, Deleanu D, Ciudin R, Ginghina C. Between Scylla and Charybdis: long-term cardiovascular complications after radiotherapy for Hodgkin's lymphoma. Hellenic J Cardiol. 2009;50: 538–543. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

