γ-H2AX as a marker for dose deposition in the brain of wistar rats after synchrotron microbeam radiation
- PMID: 25799425
- PMCID: PMC4370487
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119924
γ-H2AX as a marker for dose deposition in the brain of wistar rats after synchrotron microbeam radiation
Abstract
Objective: Synchrotron radiation has shown high therapeutic potential in small animal models of malignant brain tumours. However, more studies are needed to understand the radiobiological effects caused by the delivery of high doses of spatially fractionated x-rays in tissue. The purpose of this study was to explore the use of the γ-H2AX antibody as a marker for dose deposition in the brain of rats after synchrotron microbeam radiation therapy (MRT).
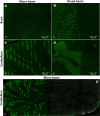
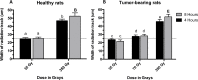
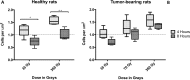
Methods: Normal and tumour-bearing Wistar rats were exposed to 35, 70 or 350 Gy of MRT to their right cerebral hemisphere. The brains were extracted either at 4 or 8 hours after irradiation and immediately placed in formalin. Sections of paraffin-embedded tissue were incubated with anti γ-H2AX primary antibody.
Results: While the presence of the C6 glioma does not seem to modulate the formation of γ-H2AX in normal tissue, the irradiation dose and the recovery versus time are the most important factors affecting the development of γ-H2AX foci. Our results also suggest that doses of 350 Gy can trigger the release of bystander signals that significantly amplify the DNA damage caused by radiation and that the γ-H2AX biomarker does not only represent DNA damage produced by radiation, but also damage caused by bystander effects.
Conclusion: In conclusion, we suggest that the γ-H2AX foci should be used as biomarker for targeted and non-targeted DNA damage after synchrotron radiation rather than a tool to measure the actual physical doses.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Bystander effects in tumor-free and tumor-bearing rat brains following irradiation by synchrotron X-rays.Int J Radiat Biol. 2013 Jun;89(6):445-53. doi: 10.3109/09553002.2013.766770. Epub 2013 Feb 26. Int J Radiat Biol. 2013. PMID: 23363251
-
Induction of DNA double-strand breaks and cellular migration through bystander effects in cells irradiated with the slit-type microplanar beam of the spring-8 synchrotron.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009 May 1;74(1):229-36. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.09.060. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009. PMID: 19362241
-
Permeability of Brain Tumor Vessels Induced by Uniform or Spatially Microfractionated Synchrotron Radiation Therapies.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2017 Aug 1;98(5):1174-1182. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.03.025. Epub 2017 Mar 21. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2017. PMID: 28721902
-
Effects of pulsed, spatially fractionated, microscopic synchrotron X-ray beams on normal and tumoral brain tissue.Mutat Res. 2010 Apr-Jun;704(1-3):160-6. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2009.12.003. Epub 2009 Dec 23. Mutat Res. 2010. PMID: 20034592 Review.
-
Nanotube x-ray for cancer therapy: a compact microbeam radiation therapy system for brain tumor treatment.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2014 Dec;14(12):1411-8. doi: 10.1586/14737140.2014.978293. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2014. PMID: 25417729 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An organotypic model for investigating drug-radiation responses in the lung.J Biol Methods. 2024 Nov 28;12(1):e99010041. doi: 10.14440/jbm.2025.0080. eCollection 2025. J Biol Methods. 2024. PMID: 40200943 Free PMC article.
-
The Microbeam Insert at the White Beam Beamline P61A at the Synchrotron PETRA III/DESY: A New Tool for High Dose Rate Irradiation Research.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 20;14(20):5137. doi: 10.3390/cancers14205137. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36291920 Free PMC article.
-
IL13RA2 targeted alpha particle therapy against glioblastomas.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 27;8(26):42997-43007. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17792. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28562337 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Microbeam Irradiation on Rodent Esophageal Smooth Muscle Contraction.Cells. 2022 Dec 31;12(1):176. doi: 10.3390/cells12010176. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36611969 Free PMC article.
-
X-rays-Induced Bystander Effect Consists in the Formation of DNA Breaks in a Calcium-Dependent Manner: Influence of the Experimental Procedure and the Individual Factor.Biomolecules. 2023 Mar 16;13(3):542. doi: 10.3390/biom13030542. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 36979480 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. World cancer report [Internet]. Boyle P, Levin B, editors. Lyon; 2008. Available: http://www.cabdirect.org/abstracts/20103010665.html
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

