N6-methyladenosine marks primary microRNAs for processing
- PMID: 25799998
- PMCID: PMC4475635
- DOI: 10.1038/nature14281
N6-methyladenosine marks primary microRNAs for processing
Abstract
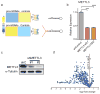
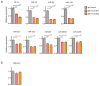
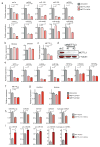
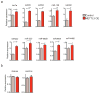
The first step in the biogenesis of microRNAs is the processing of primary microRNAs (pri-miRNAs) by the microprocessor complex, composed of the RNA-binding protein DGCR8 and the type III RNase DROSHA. This initial event requires recognition of the junction between the stem and the flanking single-stranded RNA of the pri-miRNA hairpin by DGCR8 followed by recruitment of DROSHA, which cleaves the RNA duplex to yield the pre-miRNA product. While the mechanisms underlying pri-miRNA processing have been determined, the mechanism by which DGCR8 recognizes and binds pri-miRNAs, as opposed to other secondary structures present in transcripts, is not understood. Here we find in mammalian cells that methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) methylates pri-miRNAs, marking them for recognition and processing by DGCR8. Consistent with this, METTL3 depletion reduced the binding of DGCR8 to pri-miRNAs and resulted in the global reduction of mature miRNAs and concomitant accumulation of unprocessed pri-miRNAs. In vitro processing reactions confirmed the sufficiency of the N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) mark in promoting pri-miRNA processing. Finally, gain-of-function experiments revealed that METTL3 is sufficient to enhance miRNA maturation in a global and non-cell-type-specific manner. Our findings reveal that the m(6)A mark acts as a key post-transcriptional modification that promotes the initiation of miRNA biogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

