Rotenone Stereospecifically Increases (S)-2-Hydroxyglutarate in SH-SY5Y Neuronal Cells
- PMID: 25800467
- PMCID: PMC4721232
- DOI: 10.1021/tx500535c
Rotenone Stereospecifically Increases (S)-2-Hydroxyglutarate in SH-SY5Y Neuronal Cells
Abstract
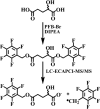
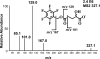
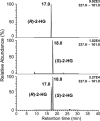
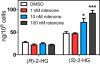
The α-ketoglutarate metabolite, 2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG), has emerged as an important mediator in a subset of cancers and rare inherited inborn errors of metabolism. Because of potential enantiospecific metabolism, chiral analysis is essential for determining the biochemical impacts of altered 2-HG metabolism. We have developed a novel application of chiral liquid chromatography-electron capture/atmospheric pressure chemical ionization/mass spectrometry, which allows for the quantification of both (R)-2-HG (D-2-HG) and (S)-2-HG (L-2-HG) in human cell lines. This method avoids the need for chiral derivatization, which could potentially distort enantiomer ratios through racemization during the derivatization process. The study revealed that the pesticide rotenone (100 nM), a mitochondrial complex I inhibitor, caused a significant almost 3-fold increase in the levels of (S)-2-HG, (91.7 ± 7.5 ng/10(6) cells) when compared with the levels of (R)-2-HG (24.1 ± 1.2 ng/10(6) cells) in the SH-SY5Y neuronal cells, a widely used model of human neurons. Stable isotope tracers and isotopologue analysis revealed that the increased (S)-2-HG was derived primarily from l-glutamine. Accumulation of highly toxic (S)-2-HG occurs in the brains of subjects with reduced L-2-HG dehydrogenase activity that results from mutations in the L2HGDH gene. This suggests that the observed stereospecific increase of (S)-2-HG in neuronal cells is due to rotenone-mediated inhibition of L-2-HG dehydrogenase but not D-2-HG dehydrogenase. The high sensitivity chiral analytical methodology that has been developed in the present study can also be employed for analyzing other disruptions to 2-HG formation and metabolism such as those resulting from mutations in the isocitrate dehydrogenase gene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


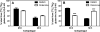
Similar articles
-
Disease-related metabolites in culture medium of fibroblasts from patients with D-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria, L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria, and combined D/L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria.Clin Chem. 2003 Jul;49(7):1133-8. doi: 10.1373/49.7.1133. Clin Chem. 2003. PMID: 12816910
-
L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria, a defect of metabolite repair.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2007 Oct;30(5):681-9. doi: 10.1007/s10545-007-0487-0. Epub 2007 Jun 21. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2007. PMID: 17603759
-
A readily 16O-/18O-isotopically-paired chiral derivatization approach for the quantification of 2-HG metabolic panel by liquid chromatography-Tandem mass spectrometry.Anal Chim Acta. 2019 Oct 24;1077:174-182. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2019.05.056. Epub 2019 May 25. Anal Chim Acta. 2019. PMID: 31307707
-
2-Hydoxyglutarate: D/Riving Pathology in gLiomaS.Brain Pathol. 2015 Nov;25(6):760-8. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12309. Brain Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26526944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
D-2-Hydroxyglutarate in Glioma Biology.Cells. 2021 Sep 7;10(9):2345. doi: 10.3390/cells10092345. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34571995 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Both Enantiomers of 2-Hydroxyglutarate Modulate the Metabolism of Cultured Human Neuroblastoma Cells.Neurochem Res. 2024 Sep;49(9):2480-2490. doi: 10.1007/s11064-024-04188-8. Epub 2024 Jun 12. Neurochem Res. 2024. PMID: 38862727 Free PMC article.
-
Oncometabolites and the response to radiotherapy.Radiat Oncol. 2020 Aug 14;15(1):197. doi: 10.1186/s13014-020-01638-9. Radiat Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32799884 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oncometabolites d- and l-2-Hydroxyglutarate Inhibit the AlkB Family DNA Repair Enzymes under Physiological Conditions.Chem Res Toxicol. 2017 Apr 17;30(4):1102-1110. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.7b00009. Epub 2017 Mar 24. Chem Res Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 28269980 Free PMC article.
-
The α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex in cancer metabolic plasticity.Cancer Metab. 2017 Feb 2;5:3. doi: 10.1186/s40170-017-0165-0. eCollection 2017. Cancer Metab. 2017. PMID: 28184304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia-Mediated Increases in L-2-hydroxyglutarate Coordinate the Metabolic Response to Reductive Stress.Cell Metab. 2015 Aug 4;22(2):291-303. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.06.021. Epub 2015 Jul 23. Cell Metab. 2015. PMID: 26212716 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

