Epigenetic changes in BRCA1-mutated familial breast cancer
- PMID: 25800897
- PMCID: PMC4466075
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cancergen.2015.02.001
Epigenetic changes in BRCA1-mutated familial breast cancer
Abstract
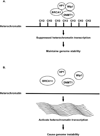
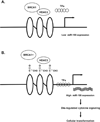
Familial breast cancer occurs in about 10% of breast cancer cases. Germline mutation in BRCA1 is the most penetrant predisposition for the disease. Mutated BRCA1 leads to disease by causing genome instability via multiple mechanisms including epigenetic changes. This review summarizes recent progress in studying the correlation between BRCA1 predisposition and epigenetic alterations in BRCA1-type familial breast cancer.
Keywords: BRCA1; autosomal dominant; epigenetic alteration; familial breast cancer; germline mutation.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer. J Clin. 2013;63(1):11–30. - PubMed
-
- U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Genetic risk assessment and BRCA mutation testing for breast and ovarian cancer susceptibility: recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2005;143(5):355–361. - PubMed
-
- Hall JM, Lee MK, Newman B, et al. Linkage of early-onset familial breast cancer to chromosome 17q21. Science. 1990;250(4988):1684–1689. - PubMed
-
- Miki Y, Swensen J, Shattuck-Eidens D, et al. A strong candidate for the breast and ovarian cancer susceptibility gene BRCA1. Science. 1994;266:66–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

