Treating diet-induced diabetes and obesity with human embryonic stem cell-derived pancreatic progenitor cells and antidiabetic drugs
- PMID: 25801507
- PMCID: PMC4400611
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2015.02.011
Treating diet-induced diabetes and obesity with human embryonic stem cell-derived pancreatic progenitor cells and antidiabetic drugs
Abstract
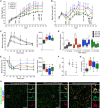
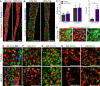
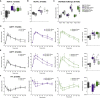
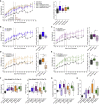
Human embryonic stem cell (hESC)-derived pancreatic progenitor cells effectively reverse hyperglycemia in rodent models of type 1 diabetes, but their capacity to treat type 2 diabetes has not been reported. An immunodeficient model of type 2 diabetes was generated by high-fat diet (HFD) feeding in SCID-beige mice. Exposure to HFDs did not impact the maturation of macroencapsulated pancreatic progenitor cells into glucose-responsive insulin-secreting cells following transplantation, and the cell therapy improved glucose tolerance in HFD-fed transplant recipients after 24 weeks. However, since diet-induced hyperglycemia and obesity were not fully ameliorated by transplantation alone, a second cohort of HFD-fed mice was treated with pancreatic progenitor cells combined with one of three antidiabetic drugs. All combination therapies rapidly improved body weight and co-treatment with either sitagliptin or metformin improved hyperglycemia after only 12 weeks. Therefore, a stem cell-based therapy may be effective for treating type 2 diabetes, particularly in combination with antidiabetic drugs.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Biarnés M., Montolio M., Nacher V., Raurell M., Soler J., Montanya E. Beta-cell death and mass in syngeneically transplanted islets exposed to short- and long-term hyperglycemia. Diabetes. 2002;51:66–72. - PubMed
-
- Brauker J., Martinson L.A., Young S.K., Johnson R.C. Local inflammatory response around diffusion chambers containing xenografts. Nonspecific destruction of tissues and decreased local vascularization. Transplantation. 1996;61:1671–1677. - PubMed
-
- Bruin J.E., Rezania A., Xu J., Narayan K., Fox J.K., O’Neil J.J., Kieffer T.J. Maturation and function of human embryonic stem cell-derived pancreatic progenitors in macroencapsulation devices following transplant into mice. Diabetologia. 2013;56:1987–1998. - PubMed
-
- Bruin J.E., Erener S., Vela J., Hu X., Johnson J.D., Kurata H.T., Lynn F.C., Piret J.M., Asadi A., Rezania A., Kieffer T.J. Characterization of polyhormonal insulin-producing cells derived in vitro from human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cell Res. (Amst.) 2014;12:194–208. - PubMed
-
- Butler A.E., Janson J., Bonner-Weir S., Ritzel R., Rizza R.A., Butler P.C. Beta-cell deficit and increased beta-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2003;52:102–110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

