Comparative efficacies of tedizolid phosphate, vancomycin, and daptomycin in a rabbit model of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis
- PMID: 25801564
- PMCID: PMC4432129
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.04376-14
Comparative efficacies of tedizolid phosphate, vancomycin, and daptomycin in a rabbit model of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis
Abstract
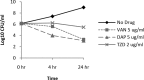
Tedizolid, the active component of the prodrug tedizolid phosphate, is a novel oxazolidinone that is approximately 4 times more active by weight than linezolid against Staphylococcus aureus in vitro. The in vivo efficacy of tedizolid phosphate (15 mg/kg body weight intravenous [i.v.] twice a day [b.i.d.]) was compared to those of vancomycin (30 mg/kg i.v. b.i.d.) and daptomycin (18 mg/kg i.v. once a day [q.d.]) in a rabbit model of aortic valve endocarditis (AVE) caused by methicillin-resistant S. aureus strain COL (infection inoculum of 10(7) CFU). Median vegetation titers of daptomycin-treated rabbits were significantly lower than those of rabbits treated with tedizolid phosphate (15 mg/kg b.i.d.) (P = 0.016), whereas titers for vancomycin-treated compared to tedizolid-treated rabbits were not different (P = 0.984). The numbers of organisms in spleen and kidney tissues were similar for all treatment groups. A dose-ranging experiment was performed with tedizolid phosphate (2, 4, and 8 mg/kg b.i.d.) compared to vancomycin (30 mg/kg b.i.d.), using a higher infecting inoculum (10(8) CFU) to determine the lowest efficacious dose of tedizolid phosphate. Tedizolid phosphate (2 mg/kg) (equivalent to 60% of the area under the concentration-time curve from 0 to 24 h (AUC0-24) for the human 200-mg dose approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration) was not efficacious. Tedizolid phosphate at 4 mg/kg (equivalent to 75% of the AUC0-24 for the human 400-mg dose) and 8 mg/kg produced lower vegetation titers than the control, but neither was as efficacious as vancomycin.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of Tedizolid Phosphate on Survival Outcomes and Suppression of Production of Staphylococcal Toxins in a Rabbit Model of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Necrotizing Pneumonia.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Mar 24;61(4):e02734-16. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02734-16. Print 2017 Apr. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017. PMID: 28137816 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Efficacies of Tedizolid Phosphate, Linezolid, and Vancomycin in a Murine Model of Subcutaneous Catheter-Related Biofilm Infection Due to Methicillin-Susceptible and -Resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Jul 22;60(8):5092-6. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00880-16. Print 2016 Aug. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27297485 Free PMC article.
-
Tedizolid: a novel oxazolidinone with potent activity against multidrug-resistant gram-positive pathogens.Drugs. 2015 Feb;75(3):253-70. doi: 10.1007/s40265-015-0352-7. Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25673021 Review.
-
Efficacy of tedizolid against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Peptostreptococcus anaerobius in thigh mixed-infection mouse model.J Infect Chemother. 2017 Jun;23(6):368-373. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2017.02.013. Epub 2017 Mar 23. J Infect Chemother. 2017. PMID: 28343752
-
Tedizolid phosphate for the treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections.Drugs Today (Barc). 2014 Nov;50(11):729-37. doi: 10.1358/dot.2014.50.11.2233783. Drugs Today (Barc). 2014. PMID: 25525633 Review.
Cited by
-
Cell Membrane Adaptations Mediate β-Lactam-Induced Resensitization of Daptomycin-Resistant (DAP-R) Staphylococcus aureus In Vitro.Microorganisms. 2021 May 11;9(5):1028. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9051028. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34064631 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia.Infect Chemother. 2016 Dec;48(4):267-273. doi: 10.3947/ic.2016.48.4.267. Infect Chemother. 2016. PMID: 28032484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New-Generation Antibiotics for Treatment of Gram-Positive Infections: A Review with Focus on Endocarditis and Osteomyelitis.J Clin Med. 2021 Apr 17;10(8):1743. doi: 10.3390/jcm10081743. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33920526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New advances in management and treatment of cardiac implantable electronic devices infections.Infection. 2024 Apr;52(2):323-336. doi: 10.1007/s15010-023-02130-8. Epub 2023 Nov 24. Infection. 2024. PMID: 37996646 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[New antibacterial agents on the market and in the pipeline].Internist (Berl). 2015 Nov;56(11):1255-63. doi: 10.1007/s00108-015-3705-0. Internist (Berl). 2015. PMID: 26475603 Review. German.
References
-
- Louie A, Liu W, Kulawy R, Drusano GL. 2011. In vivo pharmacodynamics of torezolid phosphate (TR-701), a new oxazolidinone antibiotic, against methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains in a mouse thigh infection model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 55:3453–3460. doi:10.1128/AAC.01565-10. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- CLSI. 2012. Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically; approved standard—9th ed M07-A9. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, PA.