Plasma pro-endothelin-1 peptide concentrations rise in chronic kidney disease and following selective endothelin A receptor antagonism
- PMID: 25801761
- PMCID: PMC4392442
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.114.001624
Plasma pro-endothelin-1 peptide concentrations rise in chronic kidney disease and following selective endothelin A receptor antagonism
Abstract
Background: Endothelin 1 (ET-1) contributes to chronic kidney disease (CKD) development and progression, and endothelin receptor antagonists are being investigated as a novel therapy for CKD. The proET-1 peptides, endothelin-like domain peptide (ELDP) and C-terminal pro-ET-1 (CT-proET-1), are both potential biomarkers of CKD and response to therapy with endothelin antagonists.
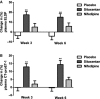
Methods and results: We assessed plasma and urine ELDP and plasma CT-proET-1 in CKD patients with minimal comorbidity. Next, in a randomized double-blind crossover study of 27 subjects with proteinuric CKD, we examined the effects of 6 weeks of treatment with placebo, sitaxentan (endothelin A antagonist), and nifedipine on these peptides alongside the primary end points of proteinuria, blood pressure, and arterial stiffness. Plasma ELDP and CT-proET-1 increased with CKD stage (both P<0.0001), correlating inversely with estimated glomerular filtration rate (both P<0.0001). Following intervention, placebo and nifedipine did not affect plasma and urine ELDP or plasma CT-proET-1. Sitaxentan increased both plasma ELDP and CT-proET-1 (baseline versus week 6±SEM: ELDP, 11.8±0.5 versus 13.4±0.6 fmol/mL; CT-proET-1, 20.5±1.2 versus 23.3±1.5 fmol/mL; both P<0.0001). Plasma ET-1 was unaffected by any treatment. Following sitaxentan, plasma ELDP and CT-proET-1 correlated negatively with 24-hour urinary sodium excretion.
Conclusions: ELDP and CT-proET-1 increase in CKD and thus are potentially useful biomarkers of renal injury. Increases in response to endothelin A antagonism may reflect EDN1 upregulation, which may partly explain fluid retention with these agents.
Clinical trial registration: URL: www.clinicalTrials.gov Unique identifier: NCT00810732.
Keywords: CKD; antagonists; endothelin; fluid retention.
© 2015 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures


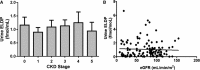



References
-
- El Nahas Meguid A, Bello AK. Chronic kidney disease: the global challenge. Lancet. 2005; 365:331-340. - PubMed
-
- Levey AS, Beto JA, Coronado BE, Eknoyan G, Foley RN, Kasiske BL, Klag MJ, Mailloux LU, Manske CL, Meyer KB, Parfrey PS, Pfeffer MA, Wenger NK, Wilson PW, Wright JT., Jr Controlling the epidemic of cardiovascular disease in chronic renal disease: What do we know? What do we need to learn? Where do we go from here? National Kidney Foundation task force on cardiovascular disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 1998; 32:853-906. - PubMed
-
- Sarnak MJ, Levey AS, Schoolwerth AC, Coresh J, Culleton B, Hamm LL, McCullough PA, Kasiske BL, Kelepouris E, Klag MJ, Parfrey P, Pfeffer M, Raij L, Spinosa DJ, Wilson PW. Kidney disease as a risk factor for development of cardiovascular disease: a statement from the American Heart Association councils on kidney in cardiovascular disease, high blood pressure research, clinical cardiology, and epidemiology and prevention. Circulation. 2003; 108:2154-2169. - PubMed
-
- Hewitt SM, Dear J, Star RA. Discovery of protein biomarkers for renal diseases. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004; 15:1677-1689. - PubMed
-
- Dhaun N, Goddard J, Webb DJ. The endothelin system and its antagonism in chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006; 17:943-955. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

