Recombinant rubella vectors elicit SIV Gag-specific T cell responses with cytotoxic potential in rhesus macaques
- PMID: 25802183
- PMCID: PMC7722989
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.02.067
Recombinant rubella vectors elicit SIV Gag-specific T cell responses with cytotoxic potential in rhesus macaques
Abstract
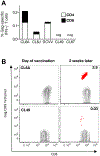
Live-attenuated rubella vaccine strain RA27/3 has been demonstrated to be safe and immunogenic in millions of children. The vaccine strain was used to insert SIV gag sequences and the resulting rubella vectors were tested in rhesus macaques alone and together with SIV gag DNA in different vaccine prime-boost combinations. We previously reported that such rubella vectors induce robust and durable SIV-specific humoral immune responses in macaques. Here, we report that recombinant rubella vectors elicit robust de novo SIV-specific cellular immune responses detectable for >10 months even after a single vaccination. The antigen-specific responses induced by the rubella vector include central and effector memory CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells with cytotoxic potential. Rubella vectors can be administered repeatedly even after vaccination with the rubella vaccine strain RA27/3. Vaccine regimens including rubella vector and SIV gag DNA in different prime-boost combinations resulted in robust long-lasting cellular responses with significant increase of cellular responses upon boost. Rubella vectors provide a potent platform for inducing HIV-specific immunity that can be combined with DNA in a prime-boost regimen to elicit durable cellular immunity.
Keywords: CM9 tetramer response; Cytotoxic T cells; DNA prime rubella boost; DNA vaccine; De novo cellular responses; HIV vaccine; IFN-γ response; Live attenuated viral vector; Memory T cells; Recall cellular responses; Rhesus macaque; Rubella prime boost; Rubella vaccine strain RA27/3; SIV Gag.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Expression of complete SIV p27 Gag and HIV gp120 engineered outer domains targeted by broadly neutralizing antibodies in live rubella vectors.Vaccine. 2017 May 31;35(24):3272-3278. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.04.047. Epub 2017 May 5. Vaccine. 2017. PMID: 28483193 Free PMC article.
-
Live attenuated rubella vectors expressing SIV and HIV vaccine antigens replicate and elicit durable immune responses in rhesus macaques.Retrovirology. 2013 Sep 16;10:99. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-10-99. Retrovirology. 2013. PMID: 24041113 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccination of Macaques with DNA Followed by Adenoviral Vectors Encoding Simian Immunodeficiency Virus (SIV) Gag Alone Delays Infection by Repeated Mucosal Challenge with SIV.J Virol. 2019 Oct 15;93(21):e00606-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00606-19. Print 2019 Nov 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31413132 Free PMC article.
-
Immunotherapy with DNA vaccine and live attenuated rubella/SIV gag vectors plus early ART can prevent SIVmac251 viral rebound in acutely infected rhesus macaques.PLoS One. 2020 Mar 4;15(3):e0228163. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228163. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32130229 Free PMC article.
-
Dendritic cell-targeted protein vaccines: a novel approach to induce T-cell immunity.J Intern Med. 2012 Feb;271(2):183-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2011.02496.x. Epub 2012 Jan 4. J Intern Med. 2012. PMID: 22126373 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
DNA Prime-Boost Vaccine Regimen To Increase Breadth, Magnitude, and Cytotoxicity of the Cellular Immune Responses to Subdominant Gag Epitopes of Simian Immunodeficiency Virus and HIV.J Immunol. 2016 Nov 15;197(10):3999-4013. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1600697. Epub 2016 Oct 12. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27733554 Free PMC article.
-
Transient T Cell Expansion, Activation, and Proliferation in Therapeutically Vaccinated Simian Immunodeficiency Virus-Positive Macaques Treated with N-803.J Virol. 2022 Dec 14;96(23):e0142422. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01424-22. Epub 2022 Nov 15. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 36377872 Free PMC article.
-
New developments in an old strategy: heterologous vector primes and envelope protein boosts in HIV vaccine design.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2016 Aug;15(8):1015-27. doi: 10.1586/14760584.2016.1158108. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2016. PMID: 26910195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of complete SIV p27 Gag and HIV gp120 engineered outer domains targeted by broadly neutralizing antibodies in live rubella vectors.Vaccine. 2017 May 31;35(24):3272-3278. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.04.047. Epub 2017 May 5. Vaccine. 2017. PMID: 28483193 Free PMC article.
-
T Lymphocytes as Measurable Targets of Protection and Vaccination Against Viral Disorders.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2019;342:175-263. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2018.07.006. Epub 2018 Oct 24. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30635091 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dai K, Liu Y, Liu M, Xu J, Huang W, Huang X, et al. Pathogenicity and immunogenicity of recombinant Tiantan Vaccinia Virus with deleted C12L and A53R genes. Vaccine. 2008;26:5062–71. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

