Plasma osteopontin in acute liver failure
- PMID: 25802196
- PMCID: PMC4587490
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2015.02.021
Plasma osteopontin in acute liver failure
Abstract
Background: Osteopontin (OPN) is a novel phosphoglycoprotein expressed in Kupffer cells that plays a pivotal role in activating natural killer cells, neutrophils and macrophages. Measuring plasma OPN levels in patients with acute liver failure (ALF) might provide insights into OPN function in the setting of massive hepatocyte injury.
Methods: OPN levels were measured using a Quantikine® ELISA assay on plasma from 105 consecutive ALF patients enrolled by the US Acute Liver Failure Study Group, as well as controls including 40 with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and 35 healthy subjects both before, and 1 and 3 days after undergoing spine fusion (SF) surgery as a model for acute inflammation.
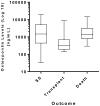
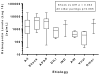
Results: Median plasma OPN levels across all etiologies of ALF patients were elevated 10- to 30-fold: overall median 1055ng/mL; range: 33-19,127), when compared to healthy controls (median in pre-SF patients: 41ng/mL; range 2.6-86.4). RA and SF post op patients had elevated OPN levels (37ng/mL and 198ng/mL respectively), well below those of the ALF patients. Median OPN levels were highest in acetaminophen (3603ng/mL) and ischemia-related ALF (4102ng/mL) as opposed to viral hepatitis (706ng/mL), drug-induced liver injury (353ng/mL) or autoimmune hepatitis (436ng/mL), correlating with the degree of hepatocellular damage, as reflected by aminotransferase values (R value: 0.47 for AST, p<0.001).
Conclusions: OPN levels appeared to correlate with degree of liver necrosis in ALF. Very high levels were associated with hyperacute injury and good outcomes. Whether OPN exerts a protective effect in limiting disease progression in this setting remains uncertain.
Keywords: Acute liver failure; Cytokine; Inflammation; Liver necrosis.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest. The authors have no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures

References
-
- Ostapowicz G, Fontana RJ, Schiødt FV, et al. Results of a prospective study of acute liver failure at 17 tertiary care centers in the United States. Ann Intern Med. 2002;137(12):947–954. - PubMed
-
- Antoniades CG, Berry PA, Wendon JA, Vergani D. The importance of immune dysfunction in determining outcome in acute liver failure. J Hepatology. 2008;49(5):845–861. - PubMed
-
- Uede T. Osteopontin, intrinsic tissue regulator of intractable inflammatory diseases. Pathol Int. 2011;61(5):265–280. - PubMed
-
- Diao H, Kon S, Iwabuchi K, et al. Osteopontin as a mediator of NKT cell function in T cell-mediated liver diseases. Immunity. 2004;21(4):539–550. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

