Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis in a child with recurrent febrile seizures
- PMID: 25802788
- PMCID: PMC4354718
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/783936
Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis in a child with recurrent febrile seizures
Abstract
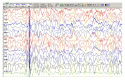
Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE) is a devastating disease of the central nervous system (CNS) caused by persistent mutant measles virus infection. The diagnosis of SSPE is based on characteristic clinical and EEG findings and demonstration of elevated antibody titres against measles in cerebrospinal fluid. Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis can have atypical clinical features at the onset. Herein, we report an unusual case of subacute sclerosing panencephalitis in a child with recurrent febrile seizures. The disease progressed with an appearance of myoclonic jerks, periodic high amplitude generalized complexes on EEG, and elevated titers of measles antibodies in cerebrospinal fluid leading to the final diagnosis of subacute sclerosing panencephalitis.
Figures
References
-
- Tuncel D., Ozbek A. E., Demirpolat G., Karabiber H. Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis with generalized seizure as the first symptom: a case report. Japanese Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2006;59(5):317–319. - PubMed
-
- Dimova P. S., Bojinova V. S. Case of subacute sclerosing panencephalitis with atypical absences and myoclonic-atonic seizures as a first symptom. Journal of Child Neurology. 2004;19(7):548–552. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources