Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis after cetuximab chemotherapy for squamous cell carcinoma of parotid gland
- PMID: 25802792
- PMCID: PMC4329742
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/530680
Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis after cetuximab chemotherapy for squamous cell carcinoma of parotid gland
Abstract
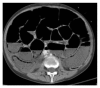
Pneumatosis intestinalis, defined as gas in the bowel wall, is often first identified on abdominal radiographs or computed tomography (CT) scans. It is a radiographic finding and not a diagnosis, as the etiology varies from benign conditions to fulminant gastrointestinal disease. We report here a case of pneumatosis intestinalis associated with cetuximab therapy for squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck. The patient underwent laparotomy based on the CT scan and the result was pneumatosis intestinalis without any signs of necrotizing enterocolitis.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources