Primary biliary cirrhosis is a generalized autoimmune epithelitis
- PMID: 25803105
- PMCID: PMC4394541
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms16036432
Primary biliary cirrhosis is a generalized autoimmune epithelitis
Abstract
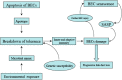
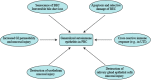
Primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) is a chronic progressive autoimmune cholestatic liver disease characterized by highly specific antimitochondrial antibodies (AMAs) and the specific immune-mediated injury of small intrahepatic bile ducts. Unique apoptotic feature of biliary epithelial cells (BECs) may contribute to apotope presentation to the immune system, causing unique tissue damage in PBC. Perpetuation of inflammation may result in senescence of BECs, contributing to irreversible loss of bile duct. In addition to the classic liver manifestations, focal inflammation and tissue damage are also seen in salivary glands and urinary tract in a significant proportion of PBC patients. These findings provide potent support to the idea that molecular mimicry may be involved in the breakdown of autoimmune tolerance and mucosal immunity may lead to a systematic epithelitis in PBC patients. Thus, PBC is considered a generalized epithelitis in clinical practice.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The immunophysiology and apoptosis of biliary epithelial cells: primary biliary cirrhosis and primary sclerosing cholangitis.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2012 Dec;43(3):230-41. doi: 10.1007/s12016-012-8324-0. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22689287 Review.
-
Infiltration of inflammatory cells expressing mitochondrial proteins around bile ducts and in biliary epithelial layer may be involved in the pathogenesis in primary biliary cirrhosis.J Clin Pathol. 2014 Jun;67(6):470-6. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2013-201917. Epub 2014 Jan 9. J Clin Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24407434
-
Primary Biliary Cholangitis: Its Pathological Characteristics and Immunopathological Mechanisms.J Med Invest. 2017;64(1.2):7-13. doi: 10.2152/jmi.64.7. J Med Invest. 2017. PMID: 28373632 Review.
-
The immunobiology and pathophysiology of primary biliary cirrhosis.Annu Rev Pathol. 2013 Jan 24;8:303-30. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-020712-164014. Annu Rev Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23347352 Review.
-
Enhanced apoptosis relates to bile duct loss in primary biliary cirrhosis.Hepatology. 1997 Dec;26(6):1399-405. doi: 10.1002/hep.510260604. Hepatology. 1997. PMID: 9397977
Cited by
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Fibrosis in Cholestatic Liver Diseases and Regenerative Medicine-Based Therapies.Cells. 2024 Dec 3;13(23):1997. doi: 10.3390/cells13231997. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39682745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hormonal contraception and the development of autoimmunity: A review of the literature.Linacre Q. 2017 Aug;84(3):275-295. doi: 10.1080/00243639.2017.1360065. Epub 2017 Aug 18. Linacre Q. 2017. PMID: 28912620 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Modifications in Generalized Autoimmune Epithelitis: Sjögren's Syndrome and Primary Biliary Cholangitis.Epigenomes. 2019 Aug 8;3(3):15. doi: 10.3390/epigenomes3030015. Epigenomes. 2019. PMID: 34968227 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Infliximab as a treatment option for patients with rheumatoid arthritis and primary biliary cirrhosis.Rheumatol Int. 2015 Nov;35(11):1913-6. doi: 10.1007/s00296-015-3366-2. Epub 2015 Sep 28. Rheumatol Int. 2015. PMID: 26411882 Review.
-
A Closer Look into Autoimmune Liver Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 21;26(5):1863. doi: 10.3390/ijms26051863. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076490 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gershwin M.E., Selmi C., Worman H.J., Gold E.B., Watnik M., Utts J., Lindor K.D., Kaplan M.M., Vierling J.M. USA PBC Epidemiology Group. Risk factors and comorbidities in primary biliary cirrhosis: A controlled interview-based study of 1032 patients. Hepatology. 2005;42:1194–1202. doi: 10.1002/hep.20907. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

