Treatment for IgG and IgA paraproteinaemic neuropathy
- PMID: 25803231
- PMCID: PMC6781839
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005376.pub3
Treatment for IgG and IgA paraproteinaemic neuropathy
Abstract
Background: Paraproteinaemic neuropathy refers to those neuropathies associated with a monoclonal gammopathy or paraprotein. The most common of these present with a chronic, predominantly sensory, symmetrical neuropathy, similar to chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (CIDP) but with relatively more sensory involvement, both clinically and neurophysiologically. The optimal treatment for neuropathies associated with IgG and IgA monoclonal gammopathy of uncertain significance is not known. This is an update of a review first published in 2007.
Objectives: To assess the effects of any treatment for IgG or IgA paraproteinaemic peripheral neuropathy.
Search methods: On 18 January 2014 we searched the Cochrane Neuromuscular Disease Group Trials Specialized Register, CENTRAL, MEDLINE and EMBASE. We also checked bibliographies for controlled trials of treatments for IgG or IgA paraproteinaemic peripheral neuropathy. We checked clinical trials registries for ongoing studies in November 2014.
Selection criteria: We considered for inclusion randomised controlled trials (RCTs) and quasi-RCTs using any treatment for IgG or IgA paraproteinaemic peripheral neuropathy. We excluded people with IgM paraproteins. We excluded people where the monoclonal gammopathy was considered secondary to an underlying disorder. We included participants of any age with a diagnosis of monoclonal gammopathy of uncertain significance with a paraprotein of the IgG or IgA class and a neuropathy. Included participants were not required to fulfil specific electrophysiological diagnostic criteria.
Data collection and analysis: We used standard Cochrane methodology to select studies, extract data and analyse results. One trial author provided additional data and clarification.
Main results: We identified one RCT, with 18 participants, that fulfilled the predetermined inclusion criteria. The trial compared plasma exchange to sham plasma exchange in participants with IgG or IgA paraproteinaemic neuropathy over a three-week follow-up period. We identified four other studies but these were not RCTs or quasi-RCTs. The included RCT did not report our predefined primary outcome measure, change in disability six months after randomisation. The trial revealed a modest benefit of plasma exchange in the weakness component of the Neuropathy Disability Score (NDS, now the Neuropathy Impairment Score); the mean improvement with plasma exchange was 17 points (95% confidence interval (CI) 5.2 to 28.8 points) versus 1 point (95% CI -7.7 to 9.7 points) in the sham exchange group at three weeks' follow-up (mean difference (MD) 16.00; 95% CI 1.37 to 30.63, low quality evidence). There was no statistically significant difference in the overall NDS (MD 18.00; 95% CI -2.03 to 38.03, low quality evidence), vibration thresholds or neurophysiological indices. Adverse events were not reported. The trial was at low risk of bias overall, although limitations of trial size and duration reduce the quality of the evidence in support of its conclusions.
Authors' conclusions: The evidence from RCTs for the treatment of IgG or IgA paraproteinaemic neuropathy is currently inadequate. More RCTs of treatments are required. These should have adequate follow-up periods and contain larger numbers of participants, perhaps through multicentre collaboration, considering the relative infrequency of this condition. Observational or open trial data provide limited support for the use of treatments such as plasma exchange, cyclophosphamide combined with prednisolone, intravenous immunoglobulin, and corticosteroids. These interventions show potential therapeutic promise but the potential benefits must be weighed against adverse effects. Their optimal use and the long-term benefits need to be considered and validated with well-designed RCTs.
Conflict of interest statement
ACJS: no disclosures.
MPTL has received honoraria for consultation from Baxter Pharmaceuticals, CSL Behring and LfB and a travel support grant from Grifols, all manufacturers of IVIG. He was a blinded investigator in the study of Comi et al 2002.
EN‐O reports personal compensation for serving in the Steering or Advisory Board of Baxter, Italy, CSL Behring, Italy, Kedrion, Italy, and Novartis, Switzerland. He received honoraria for lecturing from Baxter, Italy, CSL Behring, Italy, Grifols, Spain, and Kedrion, Italy and travel support for scientific meetings from Baxter, CSL and Kedrion. He was the principal investigator of a RCT comparing the efficacy of IVIg and intravenous methylprednisolone in a related condition, chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (CIDP), for which financial support was provided by Kedrion, Italy.
NCN: no disclosures.
This review is not compliant with the Cochrane Commercial Sponsorship policy. Future updates will have the majority of review authors and the lead author free of conflicts.
Figures




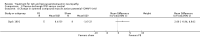
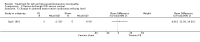
Update of
-
Treatment for IgG and IgA paraproteinaemic neuropathy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jan 24;(1):CD005376. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005376.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Mar 24;(3):CD005376. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005376.pub3. PMID: 17253554 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Dyck 1991 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Dyck P, Low PA, Windebank AJ, Jaradeh SS, Gosselin S, Bourque P, et al. Plasma exchange in polyneuropathy associated with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. New England Journal of Medicine 1991;325(21):1482‐6. [PUBMED: 1658648] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Léger 1994 {published data only}
Notermans 1996 {published data only}
-
- Notermans NC, Lokhorst HM, Franssen H, Graaf Y, Teunissen LL, Jennekens FG, et al. Intermittent cyclophosphamide and prednisone treatment of polyneuropathy associated with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. Neurology 1996;47(5):1227‐33. - PubMed
Notermans 1997 {published data only}
-
- Notermans NC, Vermeulen M, Doorn PA, Berg LH, Teunissen LL, Wokke JH. Pulsed high‐dose dexamethasone treatment of polyneuropathy associated with monoclonal gammopathy. Journal of Neurology 1997;244(7):462‐3. - PubMed
Sghirlanzoni 2000 {published data only}
-
- Sghirlanzoni A, Solari A, Ciano C, Mariotti C, Fallica E, Pareyson D. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: long‐term course and treatment of 60 patients. Neurological Sciences 2000;21(1):31‐7. - PubMed
Additional references
Bailey 1986
-
- Bailey RO, Ritaccio AL, Bishop MB, Wu AY. Benign monoclonal IgAK gammopathy associated with polyneuropathy and dysautonomia. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 1986;73(6):574‐80. - PubMed
Bleasel 1993
Bromberg 1992
-
- Bromberg MB, Feldman EL, Albers JW. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: comparison of patients with and without an associated monoclonal gammopathy. Neurology 1992;42(6):1157‐63. - PubMed
CIDP 1991
-
- Ad Hoc Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology AIDS Task Force. Research criteria for the diagnosis of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (CIDP). Neurology 1991;41(5):617‐8. - PubMed
Di Troia 1999
-
- Troia A, Carpo M, Meucci N, Pellegrino C, Allaria S, Gemignani F, et al. Clinical features and anti‐neural reactivity in neuropathy associated with IgG monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 1999;164(1):64‐71. - PubMed
Dyck 2005
-
- Dyck PJ, Boes CJ, Mulder D, Millikan C, Windebank AJ, Dyck PJ, et al. History of standard scoring, notation, and summation of neuromuscular signs. A current survey and recommendation. Journal of the Peripheral Nervous System 2005;10(2):158‐73. - PubMed
EFNS/PNS 2010
-
- Joint Task Force of the EFNS and the PNS. European Federation of Neurological Societies/Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline on the treatment of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Report of a joint task force of the European Federation of Neurological Societies and the Peripheral Nerve Society ‐ First Edition. Journal of the Peripheral Nervous System 2010;15(3):185‐95. - PubMed
Eurelings 2001
-
- Eurelings M, Notermans NC, Donk NW, Lokhorst HM. Risk factors for haematological malignancy in polyneuropathy associated with monoclonal gammopathy. Muscle & Nerve 2001;24(10):1295‐302. - PubMed
Eurelings 2002
-
- Eurelings M, Notermans NC, Wokke JH, Bosboom WM, Berg LH. Sural nerve T cells in demyelinating polyneuropathy associated with monoclonal gammopathy. Acta Neuropathologica 2002;103(2):107‐14. - PubMed
Eurelings 2003
-
- Eurelings M, Berg LH, Wokke JHJ, Franssen H, Vrancken AFJ, Notermans NC. Increase of sural nerve T cells in progressive axonal polyneuropathy and monoclonal gammopathy. Neurology 2003;61(5):707‐9. - PubMed
Fazio 1992
-
- Fazio R, Nemni R, Quattrini A, Lorenzetti I, Canal N. IgG monoclonal proteins from patients with axonal peripheral neuropathies bind to different epitopes of the 68kDa neurofilament protein. Journal of Neuroimmunology 1992;36(2‐3):97‐104. - PubMed
Gorson 1997a
Gorson 1997b
-
- Gorson KC, Allam G, Ropper AH. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: clinical features and response to treatment in 67 consecutive patients with and without a monoclonal gammopathy. Neurology 1997;48(2):321‐8. - PubMed
Gorson 2002
-
- Gorson KC, Ropper AH, Weinberg DH, Weinstein R. Efficacy of intravenous immunoglobulin in patients with IgG monoclonal gammopathy and polyneuropathy. Archives of Neurology 2002;59(5):766‐72. - PubMed
Gosselin 1991
-
- Gosselin S, Kyle RA, Dyck PJ. Neuropathy associated with monoclonal gammopathies of undetermined significance. Annals of Neurology 1991;30(1):54‐61. - PubMed
GRADEpro 2008 [Computer program]
-
- Jan Brozek, Andrew Oxman, Holger Schünemann. GRADEpro. Version 3.2 for Windows. Jan Brozek, Andrew Oxman, Holger Schünemann, 2008.
Hermosilla 1996
-
- Hermosilla E, Lagueny A, Vital C, Vital A, Ferrer X, Steck A, et al. Peripheral neuropathy associated with monoclonal IgG of undetermined significance: clinical, electrophysiologic, pathologic and therapeutic study of 14 cases. Journal of the Peripheral Nervous System 1996;1(2):139‐48. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC (editors). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011) March 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Kelly 1981
-
- Kelly JJ, Kyle RA, O'Brien P, Dyck PJ. Prevalence of monoclonal protein in peripheral neuropathy. Neurology 1981;31(11):1480‐3. - PubMed
Kiprov 2001
-
- Kiprov DD, Golden P, Rohe R, Smith S, Hofmann J, Hunnicutt J. Adverse reactions associated with mobile therapeutic apheresis: analysis of 17,940 procedures. Journal of Clinical Apheresis 2001;16(3):130‐3. - PubMed
Kleyweg 1991
-
- Kleyweg RP, Meche FG, Schmitz PI. Interobserver agreement in the assessment of muscle strength and functional abilities in Guillain‐Barre syndrome. Muscle & Nerve 1991;14(11):1103‐9. - PubMed
Kyle 1987
-
- Kyle R. Plasma cell dyscrasia: definition and diagnostic evaluation. In: Kelly J, Kyle R, Latov N editor(s). Polyneuropathies associated with plasma cell dyscrasias. Boston: Martinus Nijhoff Publishing, 1987:1‐28.
Kyle 1992
-
- Kyle RA. Diagnostic criteria of multiple myeloma. Hematology/Oncology Clinics of North America 1992;6(2):347‐58. - PubMed
Kyle 1993
-
- Kyle RA. 'Benign' monoclonal gammopathy‐after 20 to 35 years of follow up. Mayo Clinic Proceedings 1993;68(1):26‐36. - PubMed
Lunn 2012
Magy 2003
-
- Magy L, Chassande B, Maisonobe T, Bouche P, Vallat J, Léger J. Polyneuropathy associated with IgG/IgA monoclonal gammopathy: a clinical and electrophysiological study of 15 cases. European Journal of Neurology 2003;10(6):677‐85. - PubMed
Mehndiratta 2004
-
- Mehndiratta MM, Sen K, Tatke M, Bajaj BK. IgA monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance with peripheral neuropathy. Journal of Neurological Sciences 2004;221(1‐2):99‐104. - PubMed
Merkies 2000
-
- Merkies IS, Schmitz PI, Meche FG, Doorn PA, for the European Inflammatory Neuropathy Cause and Treatment (INCAT) Group. Psychometric evaluation of a new sensory scale in immune‐mediated neuropathies. Neurology 2000;54(4):943‐9. - PubMed
Merkies 2003a
Merkies 2003b
-
- Merkies IS, Schmitz PI, Meche FG, Doorn PA. Comparison between impairment and disability scales in immune‐mediated polyneuropathies. Muscle & Nerve 2003;28(1):93‐100. - PubMed
Merkies 2006
-
- Merkies IS, Lauria G. 131st ENMC international workshop: selection of outcome measures for peripheral neuropathy clinical trials 10‐12 December 2004, Narden, The Netherlands. Neuromuscular Disorders 2006;16(2):149‐56. - PubMed
Myeloma 2003
-
- International Myeloma Working Group. Criteria for the classification of monoclonal gammopathies, multiple myeloma and related disorders: a report of the International Myeloma Working Group. British Journal of Haematology 2003;121(5):749‐57. - PubMed
Nobile‐Orazio 1992
-
- Nobile‐Orazio E, Barbieri S, Baldini L, Marmiroli P, Carpo M, Premoselli S, et al. Peripheral neuropathy in monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance: prevalence and immunopathogenic studies. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 1992;85(6):383‐90. - PubMed
Nobile‐Orazio 2002
-
- Nobile‐Orazio E, Casellato C, Troia A. Neuropathies associated with IgG and IgA monoclonal gammopathy. Revue Neurologique 2002;158(10 Pt 1):979‐87. - PubMed
Notermans 1994
-
- Notermans NC, Wokke JHJ, Lokhorst HM, Franssen H, Graaf Y, Jennekens FG. Polyneuropathy associated with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. A prospective study of the prognostic value of clinical and laboratory abnormalities. Brain 1994;117(Pt 6):1385‐93. - PubMed
Notermans 1996a
-
- Notermans NC, Wokke JHJ, Berg L, Graaf Y, Franssen H, Teunissen LL, et al. Chronic idiopathic axonal polyneuropathy. Comparison of patients with and without monoclonal gammopathy. Brain 1996;119(Pt 2):421‐7. - PubMed
Notermans 2000
-
- Notermans NC, Franssen H, Eurelings M, Graaf Y, Wokke JH. Diagnostic criteria for demyelinating polyneuropathy associated with monoclonal gammopathy. Muscle & Nerve 2000;23(1):73‐9. - PubMed
Ponsford 2000
-
- Ponsford S, Willison H, Veitch J, Morris R, Thomas PK. Long term clinical and neurophysiological follow up of patients with peripheral neuropathy associated with benign monoclonal gammopathy. Muscle & Nerve 2000;23(2):150‐2. - PubMed
Ritzmann 1975
-
- Ritzmann S, Loukas D, Sakai H, Daniels JC, Levin WC. Idiopathic (asymptomatic) monoclonal gammopathies. Archives of Internal Medicine 1975;135(1):95‐106. - PubMed
Saleun 1982
Saperstein 2001
-
- Saperstein DS, Katz JS, Amato AA, Barohn RJ. Clinical spectrum of chronic acquired demyelinating polyneuropathies. Muscle & Nerve 2001;24(3):311‐24. - PubMed
Simmons 1993
-
- Simmons Z, Albers JW, Bromberg MB, Feldman EL. Presentation and initial clinical course in patients with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: comparison of patients without and with monoclonal gammopathy. Neurology 1993;43(11):2202‐9. - PubMed
Simmons 1995
-
- Simmons Z, Albers JW, Bromberg MB, Feldman EL. Long term follow up of patients with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy, without and with monoclonal gammopathy. Brain 1995;118(Pt 2):359‐68. - PubMed
Stubbs 2003
-
- Stubbs EB, Lawlor MW, Richards MP, Siddiqui K, Fisher MA, Bhoopalam N, et al. Anti‐neurofilament antibodies in neuropathy with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance produce experimental motor nerve conduction block. Acta Neuropathologica 2003;105(2):109‐16. - PubMed
Vallat 2000
-
- Vallat J, Tabaraud F, Sindou P, Preux M, Berghe A, Steck A. Myelin widenings and MGUS‐IgA: an immunoelectronmicroscopic study. Annals of Neurology 2000;47(6):808‐11. - PubMed
Vital 2000
-
- Vital A, Lagueny A, Julien J, Farrer X, Barat M, Hermosilla E, et al. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy associated with dysglobulinaemia: a peripheral nerve biopsy study in 18 cases. Acta Neuropathologica 2000;100(1):63‐8. - PubMed
Vrethem 1993
-
- Vrethem M, Cruz M, Wen‐Xin H, Malm C, Holmgren H, Ernerudh J. Clinical, neurophysiological and immunological evidence of polyneuropathy in patients with monoclonal gammopathies. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 1993;114(2):193‐9. - PubMed
Vrethem 2010
-
- Vrethem M, Reiser N, Lauermann C, Svanborg E. Polyneuropathy associated with IgM vs IgG monoclonal gammopathy: comparison between clinical and electrophysiological findings. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 2010;122(1):52‐57. - PubMed
Yeung 1991
-
- Yeung KB, Thomas PK, King RH, Waddy H, Will RG, Hughes RA, et al. The clinical spectrum of peripheral neuropathies associated with benign monoclonal IgM, IgG and IgA paraproteinaemia. Comparative clinical, immunological and nerve biopsy findings. Journal of Neurology 1991;238(7):383‐91. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Allen 2005
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

