In vitro generation of human pluripotent stem cell derived lung organoids
- PMID: 25803487
- PMCID: PMC4370217
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.05098
In vitro generation of human pluripotent stem cell derived lung organoids
Abstract
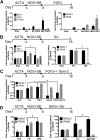
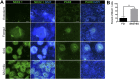
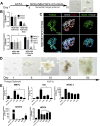
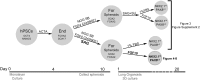
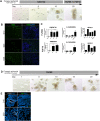
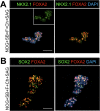
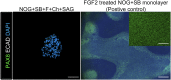
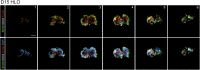
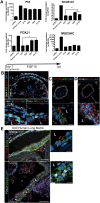
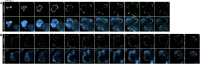
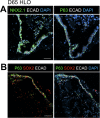
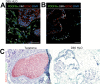
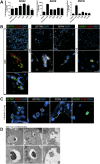
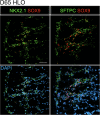
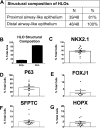
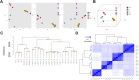
Recent breakthroughs in 3-dimensional (3D) organoid cultures for many organ systems have led to new physiologically complex in vitro models to study human development and disease. Here, we report the step-wise differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) (embryonic and induced) into lung organoids. By manipulating developmental signaling pathways hPSCs generate ventral-anterior foregut spheroids, which are then expanded into human lung organoids (HLOs). HLOs consist of epithelial and mesenchymal compartments of the lung, organized with structural features similar to the native lung. HLOs possess upper airway-like epithelium with basal cells and immature ciliated cells surrounded by smooth muscle and myofibroblasts as well as an alveolar-like domain with appropriate cell types. Using RNA-sequencing, we show that HLOs are remarkably similar to human fetal lung based on global transcriptional profiles, suggesting that HLOs are an excellent model to study human lung development, maturation and disease.
Keywords: developmental biology; endoderm; foregut; human; lung; organoids; pluripotent stem cells; spheroid; stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures
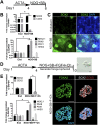
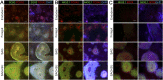
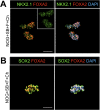

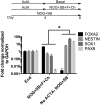

References
-
- Bellusci S, Furuta Y, Rush MG, Henderson R, Winnier G, Hogan BL. Involvement of Sonic hedgehog (Shh) in mouse embryonic lung growth and morphogenesis. Development. 1997a;124:53–63. - PubMed
-
- Bellusci S, Grindley J, Emoto H, Itoh N, Hogan BL. Fibroblast growth factor 10 (FGF10) and branching morphogenesis in the embryonic mouse lung. Development. 1997b;124:4867–4878. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

