Erythropoietin upregulates growth associated protein-43 expression and promotes retinal ganglion cell axonal regeneration in vivo after optic nerve crush
- PMID: 25806072
- PMCID: PMC4353103
- DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2012.04.010
Erythropoietin upregulates growth associated protein-43 expression and promotes retinal ganglion cell axonal regeneration in vivo after optic nerve crush
Abstract
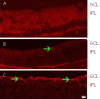
In this study, we established a rat model of optic nerve crush to explore the effects of erythropoietin on retinal ganglion cell axonal regeneration. At 15 days after injury in erythropoietin treated rats, retinal ganglion cell densities in regions corresponding to the 1/6, 3/6 and 5/6 ratios of the retinal radius were significantly increased. In addition, the number of growth associated protein-43 positive axons was significantly increased at different distances (50, 250 and 500 μm) from the crush site after erythropoietin treatment. Erythropoietin significantly increased growth associated protein-43 protein levels in the retina after crush injury, as determined by western blot and immunofluorescence analysis. These results demonstrate that erythropoietin protects injured retinal ganglion cells and promotes axonal regeneration.
Keywords: axonal regeneration; erythropoietin; neural regeneration; optic nerve crush; retinal ganglion cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Yoles E, Schwartz M. Degeneration of spared axons following partial white matter lesion: implications for optic nerve neuropathies. Exp Neurol. 1998;153(1):1–7. - PubMed
-
- Levin LA. Axonal loss and neuroprotection in optic neuropathies. Can J Ophthalmol. 2007;42(3):403–408. - PubMed
-
- Zalish M, Lavie V, Duvdevani R, et al. Gangliosides attenuate axonal loss after optic nerve injury. Retina. 1993;13(2):145–147. - PubMed
-
- Fitzgerald M, Payne SC, Bartlett CA, et al. Secondary retinal ganglion cell death and the neuroprotective effects of the calcium channel blocker lomerizine. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009;50(11):5456–5462. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
