Imaging spectrum of cerebellar pathologies: a pictorial essay
- PMID: 25806100
- PMCID: PMC4364256
- DOI: 10.12659/PJR.892878
Imaging spectrum of cerebellar pathologies: a pictorial essay
Abstract
The cerebellum is a crucial structure of hindbrain which helps in maintaining motor tone, posture, gait and also coordinates skilled voluntary movements including eye movements. Cerebellar abnormalities have different spectrum, presenting symptoms and prognosis as compared to supratentorial structures and brainstem. This article intends to review the various pathological processes involving the cerebellum along with their imaging features on MR, which are must to know for all radiologists, neurologists and neurosurgeons for their prompt diagnosis and management.
Keywords: Cerebellar Diseases; Cerebellum; Magnetic Resonance Imaging.
Figures
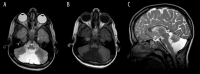
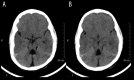
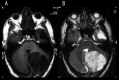
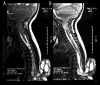
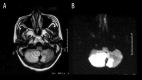
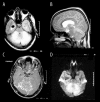

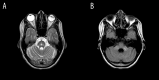
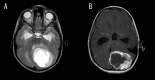

References
-
- Michael SS, Bernard LM. Brainstem and cerebellar malformations. In: Maria BL III, editor. Current management in child neurology. Hamilton, Ontario: BC Decker Inc; 2005. pp. 479–85.
-
- Kollias SS, Ball WS, Prenger EC. Cystic malformations of the posterior fossa: Differential diagnosis clarified through Embryologic Analysis. Radiographics. 1993;13:1211–31. - PubMed
-
- Ross ME, Swanson K, Dobyns WB. Lisencephaly with cerebellar hypoplasia: a heterogenous group of cortical malformations. Neuropediatrics. 2001;32:256–63. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
