Generation and expansion of highly pure motor neuron progenitors from human pluripotent stem cells
- PMID: 25806427
- PMCID: PMC4375778
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms7626
Generation and expansion of highly pure motor neuron progenitors from human pluripotent stem cells
Abstract
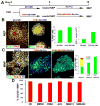
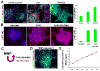
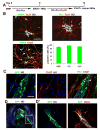
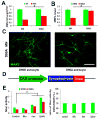
Human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) have opened new opportunities for understanding human development, modelling disease processes and developing new therapeutics. However, these applications are hindered by the low efficiency and heterogeneity of cell types, such as motorneurons (MNs), differentiated from hPSCs as well as our inability to maintain the potency of lineage-committed progenitors. Here by using a combination of small molecules that regulate multiple signalling pathways, we develop a method to guide human embryonic stem cells to a near-pure population (>95%) of motor neuron progenitors (MNPs) in 12 days, and an enriched population (>90%) of functionally mature MNs in an additional 16 days. More importantly, the MNPs can be expanded for at least five passages so that a single MNP can be amplified to 1 × 10(4). This method is reproducible in human-induced pluripotent stem cells and is applied to model MN-degenerative diseases and in proof-of-principle drug-screening assays.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Grskovic M, Javaherian A, Strulovici B, Daley GQ. Induced pluripotent stem cells--opportunities for disease modelling and drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011;10:915–929. - PubMed
-
- Han SS, Williams LA, Eggan KC. Constructing and deconstructing stem cell models of neurological disease. Neuron. 2011;70:626–644. - PubMed
-
- Kattman SJ, et al. Stage-specific optimization of activin/nodal and BMP signaling promotes cardiac differentiation of mouse and human pluripotent stem cell lines. Cell Stem Cell. 2011;8:228–240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P30 HD003352/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH099587/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- NS045926/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS074189/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS085689/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS045926/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS085689/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS076352/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HD03352/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- NS074189/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS064578/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R24 NS086604/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS064578/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

