Deregulated expression of Aurora kinases is not a prognostic biomarker in papillary thyroid cancer patients
- PMID: 25807528
- PMCID: PMC4373730
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121514
Deregulated expression of Aurora kinases is not a prognostic biomarker in papillary thyroid cancer patients
Abstract
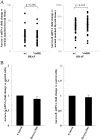
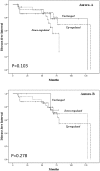
A number of reports indicated that Aurora-A or Aurora-B overexpression represented a negative prognostic factor in several human malignancies. In thyroid cancer tissues a deregulated expression of Aurora kinases has been also demonstrated, but no information regarding its possible prognostic role in differentiated thyroid cancer is available. Here, we evaluated Aurora-A and Aurora-B mRNA expression and its prognostic relevance in a series of 87 papillary thyroid cancers (PTC), with a median follow-up of 63 months. The analysis of Aurora-A and Aurora-B mRNA levels in PTC tissues, compared to normal matched tissues, revealed that their expression was either up- or down-regulated in the majority of cancer tissues. In particular, Aurora-A and Aurora-B mRNA levels were altered, respectively, in 55 (63.2%) and 79 (90.8%) out of the 87 PTC analyzed.A significant positive correlation between Aurora-A and Aurora-B mRNAs was observed (p=0.001). The expression of both Aurora genes was not affected by the BRAFV600E mutation. Univariate, multivariate and Kaplan-Mayer analyses documented the lack of association between Aurora-A or Aurora-B expression and clinicopathological parameters such as gender, age, tumor size, histology, TNM stage, lymph node metastasis and BRAF status as well as disease recurrences or disease-free interval. Only Aurora-B mRNA was significantly higher in T(3-4) tissues, with respect to T(1-2) PTC tissues. The data reported here demonstrate that the expression of Aurora kinases is deregulated in the majority of PTC tissues, likely contributing to PTC progression. However, differently from other human solid cancers, detection of Aurora-A or Aurora-B mRNAs is not a prognostic biomarker in PTC patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Trimboli P, Ulisse S, Graziano FM, Marzullo A, Ruggieri M, Calvanese A, et al. (2006) Trend in thyroid carcinoma size, age at diagnosis, and histology in a retrospective study of 500 cases diagnosed over 20 years. Thyroid 16:1151–1155. - PubMed
-
- Davies L, Welch HG (2006) Increasing incidence of thyroid cancer in the United States, 1973–2002. Jama 295:2164–2167. - PubMed
-
- Kinder B K (2003)Well differentiated thyroid cancer. Curr Opin Oncol 15:71–77. - PubMed
-
- Patel KN, Shaha AR (2006)Poorly differentiated and anaplastic thyroid cancer. Cancer Control 13:119–128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

