Dosimetric verification by using the ArcCHECK system and 3DVH software for various target sizes
- PMID: 25807544
- PMCID: PMC4373958
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119937
Dosimetric verification by using the ArcCHECK system and 3DVH software for various target sizes
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the usefulness of the 3DVH software with an ArcCHECK 3D diode array detector in newly designed plans with various target sizes.
Methods: The isocenter dose was measured with an ion-chamber and was compared with the planned and 3DVH predicted doses. The 2D gamma passing rates were evaluated at the diode level by using the ArcCHECK detector. The 3D gamma passing rates for specific regions of interest (ROIs) were also evaluated by using the 3DVH software. Several dose-volume histograms (DVH)-based predicted metrics for all structures were also obtained by using the 3DVH software.
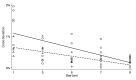
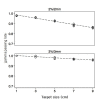
Results: The isocenter dose deviation was <1% in all plans except in the case of a 1 cm target. Besides the gamma passing rate at the diode level, the 3D gamma passing rate for specific ROIs tended to decrease with increasing target size; this was more noticeable when a more stringent gamma criterion was applied. No correlation was found with the gamma passing rates and the DVH-based metrics especially in the ROI with high-dose gradients.
Conclusions: Delivery quality assurance by using 3DVH and ArcCHECK can provide substantial information through a simple and easy approach, although the accuracy of this system should be judged cautiously.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Ezzell GA, Galvin JM, Low D, Palta JR, Rosen I, Sharpe MB, et al. Guidance document on delivery, treatment planning, and clinical implementation of IMRT: report of the IMRT Subcommittee of the AAPM Radiation Therapy Committee. Med Phys. 2003;30:2089–2115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

