Higher Alu methylation levels in catch-up growth in twenty-year-old offsprings
- PMID: 25807557
- PMCID: PMC4373937
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120032
Higher Alu methylation levels in catch-up growth in twenty-year-old offsprings
Abstract
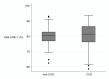
Alu elements and long interspersed element-1 (LINE-1 or L1) are two major human intersperse repetitive sequences. Lower Alu methylation, but not LINE-1, has been observed in blood cells of people in old age, and in menopausal women having lower bone mass and osteoporosis. Nevertheless, Alu methylation levels also vary among young individuals. Here, we explored phenotypes at birth that are associated with Alu methylation levels in young people. In 2010, 249 twenty-years-old volunteers whose mothers had participated in a study association between birth weight (BW) and nutrition during pregnancy in 1990, were invited to take part in our present study. In this study, the LINE-1 and Alu methylation levels and patterns were measured in peripheral mononuclear cells and correlated with various nutritional parameters during intrauterine and postnatal period of offspring. This included the amount of maternal intake during pregnancy, the mother's weight gain during pregnancy, birth weight, birth length, and the rate of weight gain in the first year of life. Catch-up growth (CUG) was defined when weight during the first year was >0.67 of the standard score, according to WHO data. No association with LINE-1 methylation was identified. The mean level of Alu methylation in the CUG group was significantly higher than those non-CUG (39.61% and 33.66 % respectively, P < 0.0001). The positive correlation between the history of CUG in the first year and higher Alu methylation indicates the role of Alu methylation, not only in aging cells, but also in the human growth process. Moreover, here is the first study that demonstrated the association between a phenotype during the newborn period and intersperse repetitive sequences methylation during young adulthood.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Methylation Status of Alu and LINE-1 Interspersed Repetitive Sequences in Behcet's Disease Patients.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:1393089. doi: 10.1155/2016/1393089. Epub 2016 Mar 30. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27123441 Free PMC article.
-
Association between birth weight and DNA methylation of IGF2, glucocorticoid receptor and repetitive elements LINE-1 and Alu.Epigenomics. 2013 Jun;5(3):271-81. doi: 10.2217/epi.13.24. Epigenomics. 2013. PMID: 23750643 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal phthalate exposure, birth outcomes and DNA methylation of Alu and LINE-1 repetitive elements: A pilot study in China.Chemosphere. 2018 Sep;206:759-765. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.030. Epub 2018 May 7. Chemosphere. 2018. PMID: 29793068
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Alu and LINE-1 Interspersed Repetitive Sequences Reveal Diseases of Visual System Dysfunction.Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2023 Nov;31(9):1848-1858. doi: 10.1080/09273948.2022.2112238. Epub 2022 Aug 30. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2023. PMID: 36040959 Review.
-
Offspring body size and metabolic profile - effects of lifestyle intervention in obese pregnant women.Dan Med J. 2014 Jul;61(7):B4893. Dan Med J. 2014. PMID: 25123127 Review.
Cited by
-
Caesarean delivery is associated with increased blood pressure in young adult offspring.Sci Rep. 2021 May 13;11(1):10201. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-89438-3. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33986334 Free PMC article.
-
Argonaute 4 as an Effector Protein in RNA-Directed DNA Methylation in Human Cells.Front Genet. 2019 Jul 4;10:645. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00645. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31333722 Free PMC article.
-
B1 siRNA Increases de novo DNA Methylation of B1 Elements and Promotes Wound Healing in Diabetic Rats.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jan 19;9:802024. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.802024. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35127718 Free PMC article.
-
The association between Alu hypomethylation and the severity of hypertension.PLoS One. 2022 Jul 8;17(7):e0270004. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0270004. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35802708 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between maternal plasma zinc concentrations in late pregnancy and LINE-1 and Alu methylation loci in the young adult offspring.PLoS One. 2022 Dec 30;17(12):e0279630. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0279630. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36584155 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chalitchagorn K, Shuangshoti S, Hourpai N, Kongruttanachok N, Tangkijvanich P, Thong-ngam D, et al. Distinctive pattern of LINE-1 methylation level in normal tissues and the association with carcinogenesis. Oncogene. 2004; 23: 8841–8846. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

