Voxel-based morphometric magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) postprocessing in MRI-negative epilepsies
- PMID: 25807928
- PMCID: PMC4447617
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.24407
Voxel-based morphometric magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) postprocessing in MRI-negative epilepsies
Abstract
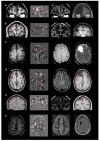
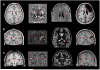
Objective: In the presurgical workup of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-negative (MRI(-) or "nonlesional") pharmacoresistant focal epilepsy (PFE) patients, discovering a previously undetected lesion can drastically change the evaluation and likely improve surgical outcome. Our study utilizes a voxel-based MRI postprocessing technique, implemented in a morphometric analysis program (MAP), to facilitate detection of subtle abnormalities in a consecutive cohort of MRI(-) surgical candidates.
Methods: Included in this retrospective study was a consecutive cohort of 150 MRI(-) surgical patients. MAP was performed on T1-weighted MRI, with comparison to a scanner-specific normal database. Review and analysis of MAP were performed blinded to patients' clinical information. The pertinence of MAP(+) areas was confirmed by surgical outcome and pathology.
Results: MAP showed a 43% positive rate, sensitivity of 0.9, and specificity of 0.67. Overall, patients with the MAP(+) region completely resected had the best seizure outcomes, followed by the MAP(-) patients, and patients who had no/partial resection of the MAP(+) region had the worst outcome (p < 0.001). Subgroup analysis revealed that visually identified subtle findings are more likely correct if also MAP(+) . False-positive rate in 52 normal controls was 2%. Surgical pathology of the resected MAP(+) areas contained mainly non-balloon-cell focal cortical dysplasia (FCD). Multiple MAP(+) regions were present in 7% of patients.
Interpretation: MAP can be a practical and valuable tool to: (1) guide the search for subtle MRI abnormalities and (2) confirm visually identified questionable abnormalities in patients with PFE due to suspected FCD. A MAP(+) region, when concordant with the patient's electroclinical presentation, should provide a legitimate target for surgical exploration.
© 2015 American Neurological Association.
Figures




References
-
- Bien CG. Characteristics and surgical outcomes of patients with refractory magnetic resonance imaging-negative epilepsies. Arch Neurol. 2009;66:1491–9. - PubMed
-
- Jeha LE. Surgical outcome and prognostic factors of frontal lobe epilepsy surgery. Brain. 2007;130:574–84. - PubMed
-
- Tellez-Zenteno JF, Hernandez Ronquillo L, Moien-Afshari F, Wiebe S. Surgical outcomes in lesional and non-lesional epilepsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Epilepsy Res. 2010 May;89(2-3):310–8. - PubMed
-
- Wang ZI, Alexopoulos AV, Jones SE, Jaisani Z, Najm IM, Prayson RA. The pathology of magnetic-resonance-imaging-negative epilepsy. Mod Pathol. 2013 Aug;26(8):1051–8. - PubMed
-
- Hauptman JS, Mathern GW. Surgical treatment of epilepsy associated with cortical dysplasia: 2012 update. Epilepsia. 2012 Sep;53(Suppl 4):98–104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

