Specific Preferences in Lineage Choice and Phenotypic Plasticity of Glioma Stem Cells Under BMP4 and Noggin Influence
- PMID: 25808628
- PMCID: PMC8029422
- DOI: 10.1111/bpa.12263
Specific Preferences in Lineage Choice and Phenotypic Plasticity of Glioma Stem Cells Under BMP4 and Noggin Influence
Abstract
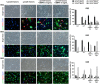
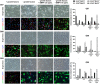
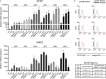
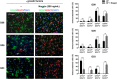
Although BMP4-induced differentiation of glioma stem cells (GSCs) is well recognized, details of the cellular responses triggered by this morphogen are still poorly defined. In this study, we established several GSC-enriched cell lines (GSC-ECLs) from high-grade gliomas. The expansion of these cells as adherent monolayers, and not as floating neurospheres, enabled a thorough study of the phenotypic changes that occurred during their differentiation. Herein, we evaluated GSC-ECLs' behavior toward differentiating conditions by depriving them of growth factors and/or by adding BMP4 at different concentrations. After analyzing cellular morphology, proliferation and lineage marker expression, we determined that GSC-ECLs have distinct preferences in lineage choice, where some of them showed an astrocyte fate commitment and others a neuronal one. We found that this election seems to be dictated by the expression pattern of BMP signaling components present in each GSC-ECL. Additionally, treatment of GSC-ECLs with the BMP antagonist, Noggin, also led to evident phenotypic changes. Interestingly, under certain conditions, some GSC-ECLs adopted an unexpected smooth muscle-like phenotype. As a whole, our findings illustrate the wide differentiation potential of GSCs, highlighting their molecular complexity and paving a way to facilitate personalized differentiating therapies.
Keywords: BMP4; Noggin; cancer stem cells; differentiation; glioblastoma; multipotency.
© 2015 International Society of Neuropathology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

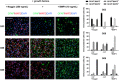
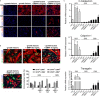

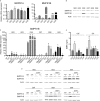
References
-
- Assinder SJ, Stanton JA, Prasad PD (2009) Transgelin: an actin‐binding protein and tumour suppressor. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41:482–486. - PubMed
-
- Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, Hao Y, Shi Q, Hjelmeland AB et al (2006) Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature 444:756–760. - PubMed
-
- Berggren P, Kumar R, Sakano S, Hemminki L, Wada T, Steineck G et al (2003) Detecting homozygous deletions in the CDKN2A[p16(INK4a)]/ARF[p14(ARF)] gene in urinary bladder cancer using real‐time quantitative PCR. Clin Cancer Res 9:235–242. - PubMed
-
- Bjornson CR, Rietze RL, Reynolds BA, Magli MC, Vescovi AL (1999) Turning brain into blood: a hematopoietic fate adopted by adult neural stem cells in vivo . Science 283:534–537. - PubMed
-
- Bonaguidi MA, McGuire T, Hu M, Kan L, Samanta J, Kessler JA (2005) LIF and BMP signaling generate separate and discrete types of GFAP‐expressing cells. Development 132:5503–5514. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

