Mitochondrial Toxicity of Cadmium Telluride Quantum Dot Nanoparticles in Mammalian Hepatocytes
- PMID: 25809595
- PMCID: PMC4476459
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfv068
Mitochondrial Toxicity of Cadmium Telluride Quantum Dot Nanoparticles in Mammalian Hepatocytes
Abstract
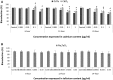
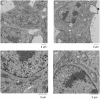
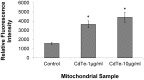
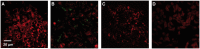
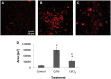
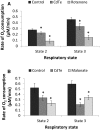
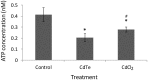
There are an increasing number of studies indicating that mitochondria are relevant targets in nanomaterial-induced toxicity. However, the underlying mechanisms by which nanoparticles (NPs) interact with these organelles and affect their functions are unknown. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of cadmium telluride quantum dot (CdTe-QD) NPs on mitochondria in human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. CdTe-QD treatment resulted in the enlargement of mitochondria as examined with transmission electron microscopy and confocal microscopy. CdTe-QDs appeared to associate with the isolated mitochondria as detected by their inherent fluorescence. Further analyses revealed that CdTe-QD caused disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential, increased intracellular calcium levels, impaired cellular respiration, and decreased adenosine triphosphate synthesis. The effects of CdTe-QDs on mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation were evidenced by changes in levels and activities of the enzymes of the electron transport chain. Elevation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator levels after CdTe-QD treatment suggested the effects of CdTe-QDs on mitochondrial biogenesis. Our results also showed that the effects of CdTe-QDs were similar or greater to those of cadmium chloride at equivalent concentrations of cadmium, suggesting that the toxic effects of CdTe-QDs were not solely due to cadmium released from the NPs. Overall, the study demonstrated that CdTe-QDs induced multifarious toxicity by causing changes in mitochondrial morphology and structure, as well as impairing their function and stimulating their biogenesis.
Keywords: cadmium telluride quantum dots; cellular respiration; electron transport chain; hepatocytes; membrane potential; mitochondria.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society of Toxicology.
Figures


References
-
- Adiele R. C., Stevens D., Kamunde C. (2012). Differential inhibition of electron transport chain enzyme complexes by cadmium and calcium in isolated rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) hepatic mitochondria. Toxicol. Sci. 127, 110–119. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong J. S. (2006). Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization: The sine qua non for cell death. Bioessays 28, 253–260. - PubMed
-
- Baratli Y., Charles A. L., Wolff V., Ben Tahar L., Smiri L., Bouitbir J., Zoll J., Piquard F., Tebourbi O., Sakly M., et al. (2013). Impact of iron oxide nanoparticles on brain, heart, lung, liver, and kidneys mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes activities and coupling. Toxicol. in vitro 27, 2142–2148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

