Evaluation of the prognostic value and functional roles of CD44v6 in gastric cancer
- PMID: 25809905
- PMCID: PMC11824125
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-015-1964-8
Evaluation of the prognostic value and functional roles of CD44v6 in gastric cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Tumor stem cell surface marker CD44v6, a member of the CD44 protein family, is causally involved in the metastasis of cancer. Little is known about the functions of CD44v6 in gastric cancer. The aim of this study was to evaluate the prognostic value of CD44v6 and investigate its functional roles.
Methods: The expression of CD44v6 in 208 primary gastric adenocarcinoma patient samples was examined using immunohistochemistry and its correlation with clinicopathological parameters, and 5-year patient survival was assessed. Two pairs of MGC-803 stable cells with either CD44v6 overexpression or knockdown were created. The effect of CD44v6 on cell proliferation, colony formation, migration and apoptosis was investigated using these two pairs of cells.
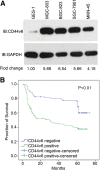
Results: Overexpression of CD44v6 was observed in all cancer cell lines. The 5-year survival rate of patients with positive CD44v6 expression is significantly worse compared to those with negative expression (38.8 vs. 73.6 %). CD44v6 and TNM stage are two independent prognostic factors of primary gastric adenocarcinoma. The risk factors for the positive CD44v6 expression are location of tumor, depth of invasion, lymph node metastasis, Lauren classification and TNM stage. In MGC-803 cells, CD44 stimulated proliferation and colony formation, antagonized oxaliplatin-induced apoptosis, but did not affect migration.
Conclusion: CD44v6 is an important prognosis marker in gastric cancer. Tissue specificity may affect the functions of CD44v6, and further work is needed to elucidate its regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors claim no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of cancer stem cell markers CD44 and CD133 in patients with gastric cancer: A comprehensive meta-analysis with 4729 patients involved.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Oct;95(42):e5163. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005163. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27759647 Free PMC article.
-
Lysyl oxidase-like 4 (LOXL4) promotes proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer via FAK/Src pathway.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015 Feb;141(2):269-81. doi: 10.1007/s00432-014-1823-z. Epub 2014 Sep 14. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25216702 Free PMC article.
-
LASP-1 promotes tumor proliferation and metastasis and is an independent unfavorable prognostic factor in gastric cancer.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2014 Nov;140(11):1891-9. doi: 10.1007/s00432-014-1759-3. Epub 2014 Jul 3. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24990592 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic Inflammation Response Index (SIRI), cancer stem cells and survival of localised gastric adenocarcinoma after curative resection.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2017 Dec;143(12):2455-2468. doi: 10.1007/s00432-017-2506-3. Epub 2017 Aug 21. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28828692 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular-targeted first-line therapy for advanced gastric cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jul 19;7(7):CD011461. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011461.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27432490 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
CD44 is a prognostic biomarker and correlated with immune infiltrates in gastric cancer.BMC Med Genomics. 2022 Oct 31;15(1):225. doi: 10.1186/s12920-022-01383-w. BMC Med Genomics. 2022. PMID: 36316684 Free PMC article.
-
CD44v6-mediated regulation of gastric cancer stem cells: a potential therapeutic target.Clin Exp Med. 2025 Mar 12;25(1):80. doi: 10.1007/s10238-025-01611-4. Clin Exp Med. 2025. PMID: 40069421 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and prognostic significances of cancer stem cell markers in gastric cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Feb 27;21(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-01840-z. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 33639931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic impact of CD44-positive cancer stem-like cells at the invasive front of gastric cancer.Br J Cancer. 2017 Jan 17;116(2):186-194. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2016.401. Epub 2016 Dec 8. Br J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 27931044 Free PMC article.
-
CD44 correlates with clinicopathological characteristics and is upregulated by EGFR in breast cancer.Int J Oncol. 2016 Oct;49(4):1343-50. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3639. Epub 2016 Jul 29. Int J Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27499099 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Afify A, Purnell P, Nguyen L (2009) Role of CD44 s and CD44v6 on human breast cancer cell adhesion, migration, and invasion. Exp Mol Pathol 86:95–100. doi:10.1016/j.yexmp.2008.12.003 - PubMed
-
- Aruffo A, Stamenkovic I, Melnick M, Underhill CB, Seed B (1990) CD44 is the principal cell surface receptor for hyaluronate. Cell 61:1303–1313. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(90)90694-A - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

