Identification and quantitative mRNA analysis of a novel splice variant of GPIHBP1 in dairy cattle
- PMID: 25810903
- PMCID: PMC4373091
- DOI: 10.1186/2049-1891-5-50
Identification and quantitative mRNA analysis of a novel splice variant of GPIHBP1 in dairy cattle
Abstract
Background: Identification of functional genes affecting milk production traits is very crucial for improving breeding efficiency in dairy cattle. Many potential candidate genes have been identified through our previous genome wide association study (GWAS). Of these, GPIHBP1 is an important novel candidate gene for milk production traits. However, the mRNA structure of the bovine GPIHBP1 gene is not fully determined up to now.
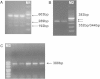
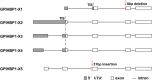
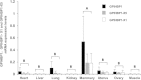
Results: In this study, we identified a novel alternatively splice transcript variant (X5) which leads to a 31 bp insertion in exon 3 and also confirmed the other four existed transcripts (X1, X2, X3 and X4) of the bovine GPIHBP1 gene. We showed that transcript X5 with a 31 bp insertion and transcript X1 with an 8 bp deletion might have tremendous effect on the protein function and structure of GPIHBP1, respectively. With semi-quantitative PCR and quantitative real-time RT-PCR, we found that the mRNA expression of GPIHBP1, GPIHBP1-X1 and GPIHBP1-X5 in mammary gland of lactating cows were much higher than that in other tissues.
Conclusions: Our study reports a novel alternative splicing of GPIHBP1 in bovine for the first time and provide useful information for the further functional analyses of GPIHBP1 in dairy cattle.
Keywords: Alternative splice variant; Cattle; Expression pattern; GPIHBP1.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification and expression pattern of two novel alternative splicing variants of EEF1D gene of dairy cattle.Gene. 2014 Jan 25;534(2):189-96. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.10.061. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Gene. 2014. PMID: 24239553
-
Role of GPIHBP1 in regulating milk protein traits in dairy cattle.Anim Biotechnol. 2020 Feb;31(1):81-85. doi: 10.1080/10495398.2018.1536064. Epub 2018 Dec 20. Anim Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 30570382
-
Functional validation of GPIHBP1 and identification of a functional mutation in GPIHBP1 for milk fat traits in dairy cattle.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 17;7(1):8546. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-08668-6. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28819221 Free PMC article.
-
Non-lactational traits of importance in dairy cows and applications for emerging biotechnologies.N Z Vet J. 2005 Dec;53(6):406-15. doi: 10.1080/00480169.2005.36585. N Z Vet J. 2005. PMID: 16317441 Review.
-
Symposium review: Genetics, genome-wide association study, and genetic improvement of dairy fertility traits.J Dairy Sci. 2019 Apr;102(4):3735-3743. doi: 10.3168/jds.2018-15269. Epub 2018 Sep 27. J Dairy Sci. 2019. PMID: 30268602 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and characterization of alternative splicing variants of buffalo LXRα expressed in mammary gland.Sci Rep. 2022 Jun 22;12(1):10588. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-14771-0. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35732883 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Franssen R, Young SG, Peelman F, Hertecant J, Sierts JA, Schimmel AW, Bensadoun A, Kastelein JJ, Fong LG, Dallinga-Thie GM, Beigneux AP. Chylomicronemia with low postheparin lipoprotein lipase levels in the setting of GPIHBP1 defects. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2010;3(2):169–178. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.109.908905. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

