Metaprop: a Stata command to perform meta-analysis of binomial data
- PMID: 25810908
- PMCID: PMC4373114
- DOI: 10.1186/2049-3258-72-39
Metaprop: a Stata command to perform meta-analysis of binomial data
Abstract
Background: Meta-analyses have become an essential tool in synthesizing evidence on clinical and epidemiological questions derived from a multitude of similar studies assessing the particular issue. Appropriate and accessible statistical software is needed to produce the summary statistic of interest.
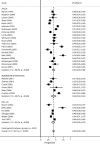
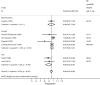
Methods: Metaprop is a statistical program implemented to perform meta-analyses of proportions in Stata. It builds further on the existing Stata procedure metan which is typically used to pool effects (risk ratios, odds ratios, differences of risks or means) but which is also used to pool proportions. Metaprop implements procedures which are specific to binomial data and allows computation of exact binomial and score test-based confidence intervals. It provides appropriate methods for dealing with proportions close to or at the margins where the normal approximation procedures often break down, by use of the binomial distribution to model the within-study variability or by allowing Freeman-Tukey double arcsine transformation to stabilize the variances. Metaprop was applied on two published meta-analyses: 1) prevalence of HPV-infection in women with a Pap smear showing ASC-US; 2) cure rate after treatment for cervical precancer using cold coagulation.
Results: The first meta-analysis showed a pooled HPV-prevalence of 43% (95% CI: 38%-48%). In the second meta-analysis, the pooled percentage of cured women was 94% (95% CI: 86%-97%).
Conclusion: By using metaprop, no studies with 0% or 100% proportions were excluded from the meta-analysis. Furthermore, study specific and pooled confidence intervals always were within admissible values, contrary to the original publication, where metan was used.
Keywords: Binomial; Confidence intervals; Freeman-Tukey double arcsine transformation; Logistic-normal; Meta-analysis; Stata.
Figures

References
-
- Agresti A, Coull BA. Approximate is better than ’exact’ for interval estimation of binomial proportions. Am Stat. 1998;52(2):119–126.
-
- Breslow NE, Clayton DG. Approximate inference in generalized linear mixed models. J Am Stat Assoc. 1993;88:9–25.
-
- Miller JJ. The inverse of the Freeman-Tukey double arcsine transformation. Am Stat. 1978;32(4):138.
-
- Molenberghs G, Verbeke G, Iddib S, Demétrio CGB. A combined beta and normal random-effects model for repeated, over-dispersed binary and binomial data. J Multivar Anal. 2012;111:94–109. doi: 10.1016/j.jmva.2012.05.005. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

