Methimazole associated neutropenia in a preterm neonate treated for hyperthyroidism
- PMID: 25810932
- PMCID: PMC4355342
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/680191
Methimazole associated neutropenia in a preterm neonate treated for hyperthyroidism
Abstract
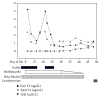
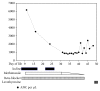
Maternal Graves' disease is relatively uncommon with an estimated incidence of 0.4%-1% of all pregnancies, but only 1-5% of newborns delivered to mothers with Graves' disease develop overt clinical signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism. Here, we describe a case of a 1380-gram female neonate who was born at 30-week gestation to a mother with Graves' disease. Our patient presented with hyperthyroidism followed by transient hypothyroidism requiring treatment with levothyroxine. While hyperthyroid, she was treated with methimazole, iodine, and a beta-blocker. 20 days after the initiation of methimazole, she developed neutropenia. The neutrophil counts started to improve immediately after the initiation of the weaning of methimazole. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case reported in the literature of methimazole induced neutropenia in a preterm infant being treated for neonatal Graves' disease.
Figures
References
-
- Bahn R. S., Burch H. S., Cooper D. S., et al. The Role of Propylthiouracil in the Management of Graves’ Disease in Adults: report of a meeting jointly sponsored by the American Thyroid Association and the Food and Drug Administration. Thyroid. 2009;19(7):673–674. doi: 10.1089/thy.2009.0169. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

