Association of endothelial nitric oxide synthase Glu298Asp gene polymorphism in psoriasis cases with hypertension
- PMID: 25811208
- PMCID: PMC6152563
- DOI: 10.5144/0256-4947.2014.340
Association of endothelial nitric oxide synthase Glu298Asp gene polymorphism in psoriasis cases with hypertension
Abstract
Background and objectives: Psoriasis is a common autoimmune-mediated chronic, inflammatory skin disease. Although, the molecular mechanism is not completely understood, psoriasis is caused by genetic and non-genetic parameters. The current study aimed (1) to define genotype and allele frequency of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS Glu298Asp) gene polymorphism in hypertensive and/or non-hypertensive psoriatic patients (2) to investigate the possible relationship between the eNOS Glu298Asp polymorphism and the risk of hypertension among psoriatic patients in the Turkish population.
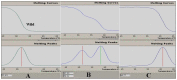
Design and settings: This cross-sectional, case-control study was performed between March 2010 and November 2012 at the University hospital in Çanakkale, Turkey Patients and Methods: Gene profiles of 75 psoriatic patients (21 hypertensive and 54 normotensive pa.tients) and 55 healthy (normotensive and non-psoriatic) volunteers were compared. Peripheral blood-EDTA samples were used for total genomic DNA isolation and genotyping. Target eNOS gene was genotyped for patients and control groups by real-time PCR melting-curve analysis system (LightCycler 2.0,Roche, Germany, and results were compared statistically.
Results: An increased T allele frequency in eNOS Glu298Asp single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) was determined in psoriatic patients when compared with normotensive non-psoriatic healthy volunteers (OR 2.3, CI 1.14-3.99), (P=.017). The T allele frequency was also found to be increased in hypertensive psoriatic patients when compared with healthy volunteers (4.83-fold increased, 95% CI 1.62-14.43 ([P=.003]) and normotensive psoriatic patients (3.03-fold increased, 95% CI 1.03-8.94 [P=.041]), respectively.
Conclusion: The current preliminary results suggested that there was a correlation between eNOS Glu298Asp polymorphism and hypertension among psoriatic patients in the Turkish population. The T allele frequency of eNOS Glu298Asp SNP was different in hypertensive psoriatic patients, and the difference was statistically significant when compared with the normotensive psoriatic patients and healthy controls. These results need to be confirmed by large-scale studies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
No evidence for an association between the Glu298Asp polymorphism of the endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene and fibromyalgia syndrome.Rheumatol Int. 2007 Jan;27(3):275-80. doi: 10.1007/s00296-006-0199-z. Epub 2006 Sep 2. Rheumatol Int. 2007. PMID: 16951945
-
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene Glu298Asp polymorphism is associated with Behçet's disease.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2006 Sep-Oct;24(5 Suppl 42):S79-82. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2006. PMID: 17067432
-
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase Glu298Asp gene polymorphism in periodontal diseases.J Periodontol. 2006 Aug;77(8):1348-54. doi: 10.1902/jop.2006.050320. J Periodontol. 2006. PMID: 16881803
-
Association between endothelial nitric oxide synthase Glu298Asp gene polymorphism and diabetic nephropathy susceptibility.Ren Fail. 2013;35(1):173-8. doi: 10.3109/0886022X.2012.734939. Epub 2012 Nov 1. Ren Fail. 2013. PMID: 23113598 Review.
-
Association of endothelial nitric oxide synthase Glu298Asp gene polymorphism with the risk of end-stage renal disease.Ren Fail. 2013;35(4):573-8. doi: 10.3109/0886022X.2013.773834. Epub 2013 Mar 7. Ren Fail. 2013. PMID: 23464568 Review.
Cited by
-
Cognitive Process of Psoriasis and Its Comorbidities: From Epidemiology to Genetics.Front Genet. 2021 Nov 26;12:735124. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.735124. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34899832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of neutrophil extracellular traps genes as potential biomarkers in psoriasis based on bioinformatics analysis.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 11;14(1):23848. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-75069-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39394253 Free PMC article.
-
Psoriasis and Cardiometabolic Diseases: Shared Genetic and Molecular Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 13;23(16):9063. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169063. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review on the Role of Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid (EDTA) in the Treatment and Understanding of Psoriasis.Cureus. 2021 Jul 16;13(7):e16424. doi: 10.7759/cureus.16424. eCollection 2021 Jul. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34277313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of the Potential Genetic Links between Psoriasis and Cardiovascular Risk Factors.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 23;22(16):9063. doi: 10.3390/ijms22169063. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445769 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Prodanovich S, Kirsner RS, Kravetz JD, Ma F, Martinez L, Federman DG. Association of psoriasis with coronary artery, cerebrovascular and peripheral vascular diseases and mortality. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145(6):700–703. - PubMed
-
- Driessen RJ, Boezeman JB, Van de Kerkhof PC, De Jong EM. Cardiovascular risk factors in high-need psoriasis patients and its implications for biological therapies. J Dermatol Treat. 2009;20(1):42–44. - PubMed
-
- Friedewald VE, Carter JC, Gelfand JM, Gordon KB, Gibbons GH, Grundy SM, et al. AJC Editor’s Consensus: Psoriasis and coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol. 2008;102(12):1631–1643. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical