Targeted deletion of the murine Lgr4 gene decreases lens epithelial cell resistance to oxidative stress and induces age-related cataract formation
- PMID: 25811370
- PMCID: PMC4374889
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119599
Targeted deletion of the murine Lgr4 gene decreases lens epithelial cell resistance to oxidative stress and induces age-related cataract formation
Abstract
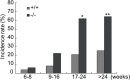
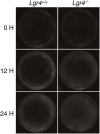
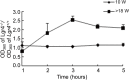
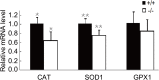
Oxidative stress contributes to the formation of cataracts. The leucine rich repeat containing G protein-coupled receptor 4 (LGR4, also known as GPR48), is important in many developmental processes. Since deletion of Lgr4 has previously been shown to lead to cataract formation in mice, we sought to determine the specific role that Lgr4 plays in the formation of cataracts. Initially, the lens opacities of Lgr4(-/-) mice at different ages without ocular anterior segment dysgenesis (ASD) were evaluated with slit-lamp biomicroscopy. Lenses from both Lgr4(-/-) and wild-type mice were subjected to oxidation induced protein denaturation to assess the ability of the lens to withstand oxidation. The expression of antioxidant enzymes was evaluated with real-time quantitative PCR. Phenotypically, Lgr4(-/-) mice showed earlier onset of lens opacification and higher incidence of cataract formation compared with wild-type mice of similar age. In addition, Lgr4(-/-) mice demonstrated increased sensitivity to environmental oxidative damage, as evidenced by altered protein expression. Real-time quantitative PCR showed that two prominent antioxidant defense enzymes, catalase (CAT) and superoxidase dismutase-1 (SOD1), were significantly decreased in the lens epithelial cells of Lgr4(-/-) mice. Our results suggest that the deletion of Lgr4 can lead to premature cataract formation, as well as progressive deterioration with aging. Oxidative stress and altered expression of several antioxidant defense enzymes contribute to the formation of cataracts.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA let-7b induces lens epithelial cell apoptosis by targeting leucine-rich repeat containing G protein-coupled receptor 4 (Lgr4) in age-related cataract.Exp Eye Res. 2016 Jun;147:98-104. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2016.04.018. Epub 2016 May 11. Exp Eye Res. 2016. PMID: 27179410
-
Targeted knockout of the mouse betaB2-crystallin gene (Crybb2) induces age-related cataract.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008 Dec;49(12):5476-83. doi: 10.1167/iovs.08-2179. Epub 2008 Aug 21. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008. PMID: 18719080
-
Does oxidative stress play any role in diabetic cataract formation? ----Re-evaluation using a thioltransferase gene knockout mouse model.Exp Eye Res. 2017 Aug;161:36-42. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2017.05.014. Epub 2017 Jun 1. Exp Eye Res. 2017. PMID: 28579033
-
Telomere Attrition in Human Lens Epithelial Cells Associated with Oxidative Stress Provide a New Therapeutic Target for the Treatment, Dissolving and Prevention of Cataract with N-Acetylcarnosine Lubricant Eye Drops. Kinetic, Pharmacological and Activity-Dependent Separation of Therapeutic Targeting: Transcorneal Penetration and Delivery of L-Carnosine in the Aqueous Humor and Hormone-Like Hypothalamic Antiaging Effects of the Instilled Ophthalmic Drug Through a Safe Eye Medication Technique.Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2016;10(2):82-129. doi: 10.2174/1872211309666150618104657. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2016. PMID: 26084629 Review.
-
Telomere-dependent senescent phenotype of lens epithelial cells as a biological marker of aging and cataractogenesis: the role of oxidative stress intensity and specific mechanism of phospholipid hydroperoxide toxicity in lens and aqueous.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2011 Apr;25(2):139-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.2010.00829.x. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 20412312 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging Roles for LGR4 in Organ Development, Energy Metabolism and Carcinogenesis.Front Genet. 2022 Jan 24;12:728827. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.728827. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35140734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LGR4 Is a Direct Target of MicroRNA-34a and Modulates the Proliferation and Migration of Retinal Pigment Epithelial ARPE-19 Cells.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 15;11(12):e0168320. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0168320. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27977785 Free PMC article.
-
Cataracts in Havanese: genome wide association study reveals two loci associated with posterior polar cataract.Canine Med Genet. 2023 Apr 28;10(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s40575-023-00127-y. Canine Med Genet. 2023. PMID: 37118843 Free PMC article.
-
GJA8 missense mutation disrupts hemichannels and induces cell apoptosis in human lens epithelial cells.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 16;9(1):19157. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-55549-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31844091 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-Seq analysis in giant pandas reveals the differential expression of multiple genes involved in cataract formation.BMC Genom Data. 2021 Oct 27;22(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s12863-021-00996-x. BMC Genom Data. 2021. PMID: 34706646 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mathias RT, Rae JL. The lens: local transport and global transparency. Exp Eye Res. 2004; 78: 689–698. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

