Dual RNA sequencing reveals the expression of unique transcriptomic signatures in lipopolysaccharide-induced BV-2 microglial cells
- PMID: 25811458
- PMCID: PMC4374676
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121117
Dual RNA sequencing reveals the expression of unique transcriptomic signatures in lipopolysaccharide-induced BV-2 microglial cells
Abstract
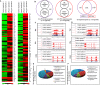
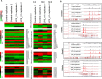
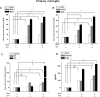
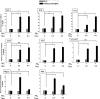
Microglial cells become rapidly activated through interactions with pathogens, and the persistent activation of these cells is associated with various neurodegenerative diseases. Previous studies have investigated the transcriptomic signatures in microglia or macrophages using microarray technologies. However, this method has numerous restrictions, such as spatial biases, uneven probe properties, low sensitivity, and dependency on the probes spotted. To overcome this limitation and identify novel transcribed genes in response to LPS, we used RNA Sequencing (RNA-Seq) to determine the novel transcriptomic signatures in BV-2 microglial cells. Sequencing assessment and quality evaluation showed that approximately 263 and 319 genes (≥ 1.5 log2-fold), such as cytokines and chemokines, were strongly induced after 2 and 4 h, respectively, and the induction of several genes with unknown immunological functions was also observed. Importantly, we observed that previously unidentified transcription factors (TFs) (irf1, irf7, and irf9), histone demethylases (kdm4a) and DNA methyltransferases (dnmt3l) were significantly and selectively expressed in BV-2 microglial cells. The gene expression levels, transcription start sites (TSS), isoforms, and differential promoter usage revealed a complex pattern of transcriptional and post-transcriptional gene regulation upon infection with LPS. In addition, gene ontology, molecular networks and pathway analyses identified the top significantly regulated functional classification, canonical pathways and network functions at each activation status. Moreover, we further analyzed differentially expressed genes to identify transcription factor (TF) motifs (-950 to +50 bp of the 5' upstream promoters) and epigenetic mechanisms. Furthermore, we confirmed that the expressions of key inflammatory genes as well as pro-inflammatory mediators in the supernatants were significantly induced in LPS treated primary microglial cells. This transcriptomic analysis is the first to show a comparison of the family-wide differential expression of most known immune genes and also reveal transcription evidence of multiple gene families in BV-2 microglial cells. Collectively, these findings reveal unique transcriptomic signatures in BV-2 microglial cells required for homeostasis and effective immune responses.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Nimmo AJ, Vink R. Recent patents in CNS drug discovery: the management of inflammation in the central nervous system. Recent Pat CNS Drug Discov. 2009;4: 86–95. - PubMed
-
- Liu B, Hong JS. Role of microglia in inflammation-mediated neurodegenerative diseases: mechanisms and strategies for therapeutic intervention. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003;304: 1–7. - PubMed
-
- Block ML, Zecca L, Hong JS. Microglia-mediated neurotoxicity: uncovering the molecular mechanisms. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8: 57–69. - PubMed
-
- Lerouge I, Vanderleyden J. O-antigen structural variation: mechanisms and possible roles in animal/plant-microbe interactions. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2002;26: 17–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

