Magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia enhances radiation therapy: A study in mouse models of human prostate cancer
- PMID: 25811736
- PMCID: PMC4696027
- DOI: 10.3109/02656736.2015.1005178
Magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia enhances radiation therapy: A study in mouse models of human prostate cancer
Abstract
Purpose: We aimed to characterise magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia (mNPH) with radiation therapy (RT) for prostate cancer.
Methods: Human prostate cancer subcutaneous tumours, PC3 and LAPC-4, were grown in nude male mice. When tumours measured 150 mm3 magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (MIONPs) were injected into tumours to a target dose of 5.5 mg Fe/cm3 tumour, and treated 24 h later by exposure to alternating magnetic field (AMF). Mice were randomly assigned to one of four cohorts to characterise (1) intratumour MIONP distribution, (2) effects of variable thermal dose mNPH (fixed AMF peak amplitude 24 kA/m at 160 ± 5 kHz) with/without RT (5 Gy), (3) effects of RT (RT5: 5 Gy; RT8: 8 Gy), and (4) fixed thermal dose mNPH (43 °C for 20 min) with/without RT (5 Gy). MIONP concentration and distribution were assessed following sacrifice and tissue harvest using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) and Prussian blue staining, respectively. Tumour growth was monitored and compared among treated groups.
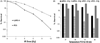
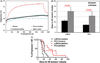
Results: LAPC-4 tumours retained higher MIONP concentration and more uniform distribution than did PC3 tumours. AMF power modulation provided similar thermal dose for mNPH and combination therapy groups (CEM43: LAPC-4: 33.6 ± 3.4 versus 25.9 ± 0.8, and PC3: 27.19 ± 0.7 versus 27.50 ± 0.6), thereby overcoming limitations of MIONP distribution and yielding statistically significant tumour growth delay.
Conclusion: PC3 and LAPC-4 tumours represent two biological models that demonstrate different patterns of nanoparticle retention and distribution, offering a model to make comparisons of these effects for mNPH. Modulating power for mNPH offers potential to overcome limitations of MIONP distribution to enhance mNPH.
Keywords: Hyperthermia; magnetic nanoparticles; prostate cancer; radiation therapy; radiosensitiser.
Conflict of interest statement
R. Ivkov is an inventor on several issued and pending patents that disclose nanoparticle formulations for imaging and hyperthermia. All patents on which R. Ivkov is an inventor are assigned to either Johns Hopkins University or Aduro Biotech. All other authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Sanda MG, Dunn RL, Michalski J, Sandler HM, Northouse L, Hembroff L, et al. Quality of life and satisfaction with outcome among prostate-cancer survivors. New Engl J Med. 2008;358:1250–1261. - PubMed
-
- Khor R, Williams S. Contemporary issues in radiotherapy for clinically Localized prostate cancer. Hematol Oncol Clin N Am. 2013;27:1137–1162. - PubMed
-
- Horsman MR, Overgaard J. Hyperthermia: A potent enhancer of radiotherapy. Clin Oncol. 2007;19:418–426. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
