Targeting AMPK for cancer prevention and treatment
- PMID: 25812084
- PMCID: PMC4480686
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.3629
Targeting AMPK for cancer prevention and treatment
Abstract
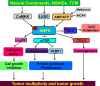
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is an important mediator in maintaining cellular energy homeostasis. AMPK is activated in response to a shortage of energy. Once activated, AMPK can promote ATP production and regulate metabolic energy. AMPK is a known target for treating metabolic syndrome and type-2 diabetes; however, recently AMPK is emerging as a possible metabolic tumor suppressor and target for cancer prevention and treatment. Recent epidemiological studies indicate that treatment with metformin, an AMPK activator reduces the incidence of cancer. In this article we review the role of AMPK in regulating inflammation, metabolism, and other regulatory processes with an emphasis on cancer, as well as, discuss the potential for targeting AMPK to treat various types of cancer. Activation of AMPK has been found to oppose tumor progression in several cancer types and offers a promising cancer therapy. This review evaluates the evidence linking AMPK with tumor suppressor function and analyzes the molecular mechanisms involved. AMPK activity opposes tumor development and progression in part by regulating inflammation and metabolism.
Keywords: AMP activated kinase; cancer; prevention; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hardie DG. AMP-activated/SNF1 protein kinases: conserved guardians of cellular energy. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology. 2007;8:774–785. - PubMed
-
- Shaw RJ, Kosmatka M, Bardeesy N, Hurley RL, Witters LA, DePinho RA, Cantley LC. The tumor suppressor LKB1 kinase directly activates AMP-activated kinase and regulates apoptosis in response to energy stress. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2004;101:3329–3335. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen Z, Shen X, Shen F, Zhong W, Wu H, Liu S, Lai J. TAK1 activates AMPK-dependent cell death pathway in hydrogen peroxide-treated cardiomyocytes, inhibited by heat shock protein-70. Molecular and cellular biochemistry. 2013;377:35–44. - PubMed
-
- Yao F, Ji GY, Zhang L. [AMPK: a novel target controlling inflammation] Sheng li xue bao: [Acta physiologica Sinica] 2012;64:341–345. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

