Synthesis and biological properties of 5-(1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)isoxazolidines: a new class of C-nucleosides
- PMID: 25812148
- PMCID: PMC6272400
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules20045260
Synthesis and biological properties of 5-(1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)isoxazolidines: a new class of C-nucleosides
Abstract
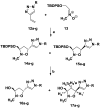
A novel series of C-nucleosides, featuring the presence of a 1,2,3-triazole ring linked to an isoxazolidine system, has been designed as mimetics of the pyrimidine nucleobases. An antiproliferative effect was observed for compounds 17a and 17b: the growth inhibitory effect reaches the 50% in HepG2 and HT-29 cells and increases up to 56% in the SH-SY5Y cell line after 72 h of incubation at a 100 µM concentration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

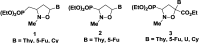




Similar articles
-
Synthesis and biological activity of new arenediyne-linked isoxazolidines.Bioorg Med Chem. 2014 Jul 1;22(13):3379-85. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2014.04.047. Epub 2014 May 4. Bioorg Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24835789
-
Design, synthesis and cytotoxicity of a new series of isoxazolidine based nucleoside analogues.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2011 May;344(5):301-10. doi: 10.1002/ardp.201000282. Epub 2011 Feb 11. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2011. PMID: 21312233
-
Synthesis and biological evaluation of 3-hydroxymethyl-5-(1H-1,2,3-triazol) isoxazolidines.Bioorg Med Chem. 2013 Dec 15;21(24):7929-37. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2013.10.001. Bioorg Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 24436994
-
Isoxazolidine: A Privileged Scaffold for Organic and Medicinal Chemistry.Chem Rev. 2016 Dec 28;116(24):15235-15283. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00543. Epub 2016 Dec 16. Chem Rev. 2016. PMID: 27981833 Review.
-
Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine (7-deazapurine) as a privileged scaffold in design of antitumor and antiviral nucleosides.Med Res Rev. 2017 Nov;37(6):1429-1460. doi: 10.1002/med.21465. Epub 2017 Aug 23. Med Res Rev. 2017. PMID: 28834581 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Modified Gold Screen-Printed Electrodes for the Determination of Heavy Metals.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Jul 30;24(15):4935. doi: 10.3390/s24154935. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39123983 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of a Red Grape Juice Extract against Bisphenol A-Induced Toxicity in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells.Toxics. 2023 Apr 21;11(4):391. doi: 10.3390/toxics11040391. Toxics. 2023. PMID: 37112618 Free PMC article.
-
Bergamottin and 5-Geranyloxy-7-methoxycoumarin Cooperate in the Cytotoxic Effect of Citrus bergamia (Bergamot) Essential Oil in Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cell Line.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Apr 10;13(4):275. doi: 10.3390/toxins13040275. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33920139 Free PMC article.
-
Design, Synthesis, and Biological Activity of New Triazole and Nitro-Triazole Derivatives as Antifungal Agents.Molecules. 2017 Jul 10;22(7):1150. doi: 10.3390/molecules22071150. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28698522 Free PMC article.
-
Chemoselective Oxidation of Isoxazolidines with Ruthenium Tetroxide: A Successful Intertwining of Combined Theoretical and Experimental Data.Molecules. 2022 Aug 24;27(17):5390. doi: 10.3390/molecules27175390. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36080160 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De Clercq E. The history of antiretrovirals: Key discoveries over the past 25 years. Rev. Med. Virol. 2009;19:287–299. - PubMed
-
- De Clercq E. Antiviral Drug Strategies. Wiley-VCH; Weinheim, Germany: 2011.
-
- Vanek V., Budesinsky M., Rinnova M., Rosenberg I. Prolinol-based nucleoside phosphonic acids: New isosteric conformationally flexible nucleotide analogues. Tetrahedron. 2009;65:862–876. doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2008.11.035. - DOI
-
- Ishitsuka H., Shimma N. Capecitabine Preclinical Studies: From Discovery to Translational Research. In: Herdewijn P., editor. Modified Nucleosides in Biochemistry, Biotechnology and Medicine. Wiley-VCH; Weinheim, Germany: 2008. pp. 587–600.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

