Synthesis and biological properties of 5-(1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)isoxazolidines: a new class of C-nucleosides
- PMID: 25812148
- PMCID: PMC6272400
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules20045260
Synthesis and biological properties of 5-(1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)isoxazolidines: a new class of C-nucleosides
Abstract
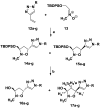
A novel series of C-nucleosides, featuring the presence of a 1,2,3-triazole ring linked to an isoxazolidine system, has been designed as mimetics of the pyrimidine nucleobases. An antiproliferative effect was observed for compounds 17a and 17b: the growth inhibitory effect reaches the 50% in HepG2 and HT-29 cells and increases up to 56% in the SH-SY5Y cell line after 72 h of incubation at a 100 µM concentration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

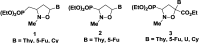




References
-
- De Clercq E. The history of antiretrovirals: Key discoveries over the past 25 years. Rev. Med. Virol. 2009;19:287–299. - PubMed
-
- De Clercq E. Antiviral Drug Strategies. Wiley-VCH; Weinheim, Germany: 2011.
-
- Vanek V., Budesinsky M., Rinnova M., Rosenberg I. Prolinol-based nucleoside phosphonic acids: New isosteric conformationally flexible nucleotide analogues. Tetrahedron. 2009;65:862–876. doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2008.11.035. - DOI
-
- Ishitsuka H., Shimma N. Capecitabine Preclinical Studies: From Discovery to Translational Research. In: Herdewijn P., editor. Modified Nucleosides in Biochemistry, Biotechnology and Medicine. Wiley-VCH; Weinheim, Germany: 2008. pp. 587–600.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

