Infectious disease. Life-threatening influenza and impaired interferon amplification in human IRF7 deficiency
- PMID: 25814066
- PMCID: PMC4431581
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aaa1578
Infectious disease. Life-threatening influenza and impaired interferon amplification in human IRF7 deficiency
Abstract
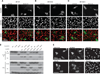
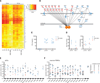
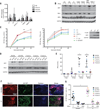
Severe influenza disease strikes otherwise healthy children and remains unexplained. We report compound heterozygous null mutations in IRF7, which encodes the transcription factor interferon regulatory factor 7, in an otherwise healthy child who suffered life-threatening influenza during primary infection. In response to influenza virus, the patient's leukocytes and plasmacytoid dendritic cells produced very little type I and III interferons (IFNs). Moreover, the patient's dermal fibroblasts and induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived pulmonary epithelial cells produced reduced amounts of type I IFN and displayed increased influenza virus replication. These findings suggest that IRF7-dependent amplification of type I and III IFNs is required for protection against primary infection by influenza virus in humans. They also show that severe influenza may result from single-gene inborn errors of immunity.
Copyright © 2015, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures

References
-
- Palese P, Shaw ML. In: Fields Virology. 5. Knipe D, Howley P, editors. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. pp. 1647–1689.
-
- Dawood FS, et al. Pediatrics. 2011;128:e27–e32. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, FluView: Influenza-Associated Hospitalization Surveillance Network. 2013 http://gis.cdc.gov/grasp/fluview/FluHospChars.html.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- 5R01NS072381/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000043/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 261299/ERC_/European Research Council/International
- R01 NS072381/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN272201400008C/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN272201400008C/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1U19AI109945/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01AI100887/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI100887/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 8UL1TR000043/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 101853/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- U19 AI109945/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

