Risk-stratified outcomes of nonmyeloablative HLA-haploidentical BMT with high-dose posttransplantation cyclophosphamide
- PMID: 25814532
- PMCID: PMC4424420
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2015-01-623991
Risk-stratified outcomes of nonmyeloablative HLA-haploidentical BMT with high-dose posttransplantation cyclophosphamide
Abstract
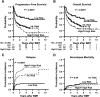
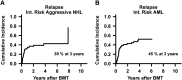
Related HLA-haploidentical blood or marrow transplantation (BMT) with high-dose posttransplantation cyclophosphamide (PTCy) is being increasingly used because of its acceptable safety profile. To better define outcomes of nonmyeloablative (NMA) HLA-haploidentical BMT with PTCy, 372 consecutive adult hematologic malignancy patients who underwent this procedure were retrospectively studied. Risk-stratified outcomes were evaluated using the refined Disease Risk Index (DRI), developed to stratify disease risk across histologies and allogeneic BMT regimens. Patients received uniform conditioning, T-cell-replete allografting, then PTCy, mycophenolate mofetil, and tacrolimus. Six-month probabilities of nonrelapse mortality and severe acute graft-versus-host disease were 8% and 4%. With 4.1-year median follow-up, 3-year probabilities of relapse, progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS) were 46%, 40%, and 50%, respectively. By refined DRI group, low (n = 71), intermediate (n = 241), and high/very high (n = 60) risk groups had 3-year PFS estimates of 65%, 37%, and 22% (P < .0001), with corresponding 3-year OS estimates of 71%, 48%, and 35% (P = .0001). On multivariable analyses, the DRI was statistically significantly associated with relapse, PFS, and OS (each P < .001). This analysis demonstrates that the DRI effectively risk stratifies recipients of NMA HLA-haploidentical BMT with PTCy and also suggests that this transplantation platform yields similar survivals to those seen with HLA-matched BMT.
© 2015 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures

References
-
- Brunstein CG, Fuchs EJ, Carter SL, et al. Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network. Alternative donor transplantation after reduced intensity conditioning: results of parallel phase 2 trials using partially HLA-mismatched related bone marrow or unrelated double umbilical cord blood grafts. Blood. 2011;118(2):282–288. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beatty PG, Clift RA, Mickelson EM, et al. Marrow transplantation from related donors other than HLA-identical siblings. N Engl J Med. 1985;313(13):765–771. - PubMed
-
- Petersdorf EW, Gooley TA, Anasetti C, et al. Optimizing outcome after unrelated marrow transplantation by comprehensive matching of HLA class I and II alleles in the donor and recipient. Blood. 1998;92(10):3515–3520. - PubMed
-
- Morishima Y, Sasazuki T, Inoko H, et al. The clinical significance of human leukocyte antigen (HLA) allele compatibility in patients receiving a marrow transplant from serologically HLA-A, HLA-B, and HLA-DR matched unrelated donors. Blood. 2002;99(11):4200–4206. - PubMed
-
- Szydlo R, Goldman JM, Klein JP, et al. Results of allogeneic bone marrow transplants for leukemia using donors other than HLA-identical siblings. J Clin Oncol. 1997;15(5):1767–1777. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

