Fluconazole-induced acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis
- PMID: 25814733
- PMCID: PMC4372937
- DOI: 10.4103/0019-5154.152572
Fluconazole-induced acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis
Abstract
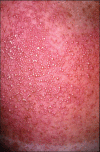
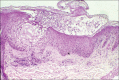
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) is a severe cutaneous adverse reaction and is usually caused by drugs. It is characterized by fever and acute, extensive occurrence of disseminated sterile pustules, accompanied by fever, malaise and peripheral blood leucocytosis. There have been several reports to date of AGEP following exposure to antifungals. In particular, terbinafine is included in the list of the agents conferring the highest risk of AGEP. The authors report the case of a 70-year-old male patient who developed AGEP shortly after commencing treatment with fluconazole, which has been reported in association with AGEP in a single case report. To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of AGEP associated with positive fluconazole patch test.
Keywords: Antifungals; drug; patch test; reaction; skin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Beylot C, Bioulac P, Doutre MS. Acute generalized exanthematic pustuloses (four cases) Ann Dermatol Venéol. 1980;107:37–48. - PubMed
-
- Roujeau JC, Bioulac-Sage P, Bourseau C, Guillaume JC, Bernard P, Lok C, et al. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. Analysis of 63 cases. Arch Dermatol. 1991;127:1333–8. - PubMed
-
- Di Lernia V, Grenzi L, Guareschi E, Ricci C. Rapid clearing of acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis after administration of ciclosporin. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34:e757–9. - PubMed
-
- Gencoglan G, Tosun M, Aktepe F. The molecular mechanism of etanercept, an anti-tumour necrosis factor-alpha receptor-fusion protein, in the treatment of acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2009;20:241–5. - PubMed
-
- Barbaud A, Collet E, Milpied B, Assier H, Staumont D, Avenel-Audran M, et al. A multicenter study to determine the value and safety of drug patch tests for the three main classes of severe cutaneous adverse drug reactions. Br J Dermatol. 2013;168:555–62. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
