Mixed-Metal Oxo Clusters Structurally Derived from Ti6O4(OR)8(OOCR')8
- PMID: 25814833
- PMCID: PMC4362470
- DOI: 10.1002/ejic.201402499
Mixed-Metal Oxo Clusters Structurally Derived from Ti6O4(OR)8(OOCR')8
Abstract
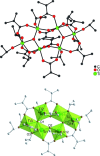
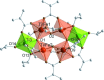
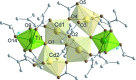
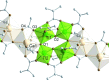
The mixed-metal oxo clusters FeTi5O4(OiPr)4(OMc)10 (OMc = methacrylate), Zn2Ti4O4(OiPr)2(OMc)10, Cd4Ti2O2(OAc)2(OMc)10(HOiPr)2, [Ca2Ti4O4(OAc)2(OMc)10] n , and [Sr2Ti4O4(OMc)12(HOMc)2] n were obtained from the reaction of titanium alkoxides with the corresponding metal acetates and methacrylic acid. Their structures are derived from Ti clusters with the composition Ti6O4(OR)8(OOCR')8. The Ca and Sr derivatives consist of chains of condensed clusters.
Keywords: Bimetallic compounds; Carboxylate ligands; Chain structures; Cluster compounds; Titanium.
Figures



References
-
- Schubert U. J. Mater. Chem. 2005;15:3701–3715.
-
- Moraru B, Hüsing N, Kickelbick G, Schubert U, Fratzl P, Peterlik H. Chem. Mater. 2002;14:2732–2740.
-
- Gautier-Luneau I, Mosset A, Galy J. Z. Kristallogr. 1987;180:83–95.
- Gautier-Luneau I, Mosset A, Galy J. Z. Kristallogr. 1987;180
- Gautier-Luneau I, Mosset A, Galy J. Z. Kristallogr. 1987;180
- Gautier-Luneau I, Mosset A, Galy J. Z. Kristallogr. 1987;180
- Gautier-Luneau I, Mosset A, Galy J. Z. Kristallogr. 1987;180
- Gautier-Luneau I, Mosset A, Galy J. Z. Kristallogr. 1987;180
- Gautier-Luneau I, Mosset A, Galy J. Z. Kristallogr. 1987;180
- Heinz P, Puchberger M, Bendova M, Baumann SO, Schubert U. Dalton Trans. 2010;39 - PubMed
-
- Moraru B, Kickelbick G, Schubert U. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2001:1295–1301.
- Jupa M, Kickelbick G, Schubert U. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2004
-
- Artner C, Czakler M, Schubert U. Chem. Eur. J. 2014;20:493–498. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
