The pattern of c-Fos expression and its refractory period in the brain of rats and monkeys
- PMID: 25814929
- PMCID: PMC4357304
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00072
The pattern of c-Fos expression and its refractory period in the brain of rats and monkeys
Abstract
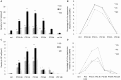
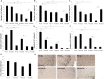
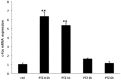
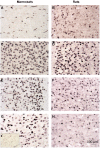
Intense activation of neurons triggers the appearance of immediate expression genes, including c-Fos. This gene is related to various signal cascades involved in biochemical processes such as neuronal plasticity, cell growth and mitosis. Here we investigate the expression pattern and the refractory period of c-Fos in rats and monkey's brains after stimulation with pentylenetetrazol. Rats and monkeys were sacrificed at various times after PTZ-induced seizure. Here we show that rats and monkeys already showed c-Fos expression at 0.5 h after seizure. Yet, the pattern of protein expression was longer in monkeys than rats, and also was not uniform (relative intensity) across different brain regions in monkeys as opposed to rats. In addition monkeys had a regional brain variation with regard to the temporal profile of c-Fos expression, which was not seen in rats. The refractory period after a second PTZ stimulation was also markedly different between rats and monkeys with the latter even showing a summatory effect on c-Fos expression after a second stimulation. However, assessment of c-Fos mRNA in rats indicated a post-transcriptional control mechanism underlying the duration of the refractory period. The difference in the protein expression pattern in rodents and primates characterizes a functional aspect of brain biochemistry that differs between these mammalian orders and may contribute for the more developed primate cognitive complexity as compared to rodents given c-Fos involvement in cognitive and learning tasks.
Keywords: brain plasticity; c-Fos expression; marmosets; neuronal activation; phylogeny.
Figures
References
-
- Baille-Le Crom V., Collombet J. M., Burckhart M. F., Foquin A., Pernot-Marino E., Rondouin G., et al. (1996). Time course and regional expression of c-Fos and HSP70 in hippocampus and piriform cortex following soman-induced seizures. J. Neurosci. Res. 45, 513–524. 10.1002/(sici)1097-4547(19960901)45:5<513::aid-jnr1>3.0.co;2-f - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bisler S., Schleicher A., Gass P., Stehe J. H., Zilles K., Staiger J. F. (2002). Expression of c-Fos, ICER, Krox-24 and JunB in the whisker-to-barrel pathway of rats: time course of induction upon whisker stimulation by tactile exploration of an enriched environment. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 23, 187–198. 10.1016/s0891-0618(01)00155-7 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Blanco M. M., dos Santos J. G., Jr., Perez-Mendes P., Kohek S. R. B., Cavarsan C. F., Hummel M., et al. (2009). Assessment of seizure susceptibility in pilocarpine epileptic and nonepileptic Wistar rats and of seizure reinduction with pentylenetetrazole and electroshock models. Epilepsia 50, 824–831. 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2008.01797.x - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

