Retinoid receptors in bone and their role in bone remodeling
- PMID: 25814978
- PMCID: PMC4356160
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2015.00031
Retinoid receptors in bone and their role in bone remodeling
Abstract
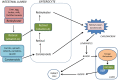
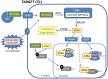
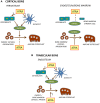
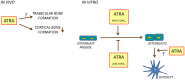
Vitamin A (retinol) is a necessary and important constituent of the body which is provided by food intake of retinyl esters and carotenoids. Vitamin A is known best for being important for vision, but in addition to the eye, vitamin A is necessary in numerous other organs in the body, including the skeleton. Vitamin A is converted to an active compound, all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA), which is responsible for most of its biological actions. ATRA binds to intracellular nuclear receptors called retinoic acid receptors (RARα, RARβ, RARγ). RARs and closely related retinoid X receptors (RXRα, RXRβ, RXRγ) form heterodimers which bind to DNA and function as ligand-activated transcription factors. It has been known for many years that hypervitaminosis A promotes skeleton fragility by increasing osteoclast formation and decreasing cortical bone mass. Some epidemiological studies have suggested that increased intake of vitamin A and increased serum levels of retinoids may decrease bone mineral density and increase fracture rate, but the literature on this is not conclusive. The current review summarizes how vitamin A is taken up by the intestine, metabolized, stored in the liver, and processed to ATRA. ATRA's effects on formation and activity of osteoclasts and osteoblasts are outlined, and a summary of clinical data pertaining to vitamin A and bone is presented.
Keywords: osteoblast; osteoclast; osteoporosis; retinoids; vitamin A.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vitamin a metabolism, action, and role in skeletal homeostasis.Endocr Rev. 2013 Dec;34(6):766-97. doi: 10.1210/er.2012-1071. Epub 2013 May 29. Endocr Rev. 2013. PMID: 23720297 Review.
-
Breast cancer progression in MCF10A series of cell lines is associated with alterations in retinoic acid and retinoid X receptors and with differential response to retinoids.Int J Oncol. 2004 Oct;25(4):961-71. Int J Oncol. 2004. PMID: 15375546
-
Combined treatment of P-gp-positive L1210/VCR cells by verapamil and all-trans retinoic acid induces down-regulation of P-glycoprotein expression and transport activity.Toxicol In Vitro. 2008 Feb;22(1):96-105. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2007.08.011. Epub 2007 Aug 31. Toxicol In Vitro. 2008. PMID: 17920233
-
RARγ is a negative regulator of osteoclastogenesis.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2015 Jun;150:46-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2015.03.005. Epub 2015 Mar 20. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25800721
-
The role of vitamin A and retinoic acid receptor signaling in post-natal maintenance of bone.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016 Jan;155(Pt A):135-46. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2015.09.036. Epub 2015 Nov 4. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26435449 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinically relevant doses of vitamin A decrease cortical bone mass in mice.J Endocrinol. 2018 Oct 31;239(3):389-402. doi: 10.1530/JOE-18-0316. J Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 30388359 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoic and ascorbic acids induce osteoblast differentiation from human dental pulp mesenchymal stem cells.J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2021 Apr-Jun;11(2):143-148. doi: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2021.01.002. Epub 2021 Jan 13. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2021. PMID: 33537186 Free PMC article.
-
Association of blood vitamin A with osteoarthritis: a nationally representative cross-sectional study.Front Nutr. 2024 Nov 5;11:1459332. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1459332. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39564209 Free PMC article.
-
The Pleiotropic Role of Retinoic Acid/Retinoic Acid Receptors Signaling: From Vitamin A Metabolism to Gene Rearrangements in Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 14;20(12):2921. doi: 10.3390/ijms20122921. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31207999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[All-trans retinoic acid and vascular endothelial growth factor induced the directional osteogenic differentiation of mouse embryonic fibroblasts].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020 Feb 15;34(2):246-255. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.201906099. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32030959 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Hopkins FG. The analyst and the medical man. Analyst (1906) 31:385–40410.1039/an906310385b - DOI
-
- McCollum EV, Simmonds N, Parsons HT. A biological analysis of pellagra-producing diets: V. The nature of the dietary deficiencies of a diet derived from peas, wheat flour, and cottonseed oil. J Biol Chem (1918) 33:411–23.
-
- Karrer P, Morf R, Schöpp K. Zur kenntnis des vitamins-A aus fischtranen. Helv Chim Acta (1931) 14(1036–40):431–610.1002/hlca.19310140622 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

