Whole-foods, plant-based diet alleviates the symptoms of osteoarthritis
- PMID: 25815212
- PMCID: PMC4359818
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/708152
Whole-foods, plant-based diet alleviates the symptoms of osteoarthritis
Abstract
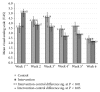
Objective. To evaluate the effectiveness of a whole-foods, plant-based diet (WFPB) to reduce symptoms of osteoarthritis. Methods. Six-week, prospective randomized open-label study of patients aged 19-70 with osteoarthritis. Participants were randomized to a WFPB (intervention) or continuing current diet (control). Outcomes were assessed by mixed models analysis of participant self-assessed weekly SF-36v2 domain t scores, weekly Patient Global Impression of Change (PGIC) scales, and mean weekly Visual Analog Scale (VAS) pain assessment. Mixed models analysis also evaluated pre-post change from baseline level for standard clinical measures: weight, BMI, body temperature, pulse, and blood pressure. Results. Forty participants were randomized. Thirty-seven of them, 18 control and 19 intervention, completed the study. The intervention group reported a significantly greater improvement than the control group in SF-36v2 energy/vitality, physical functioning, role physical, and the physical component summary scale. The differences between the intervention and control PGIC scales were statistically significant over time. Intervention group improvement in VAS weekly mean was also significantly greater than that of the control group from week 2 onward. Conclusion. Study results suggest that a whole-foods, plant-based diet significantly improves self-assessed measures of functional status among osteoarthritis patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prospective analysis of clinical evaluation and self-assessment by patients after decompression surgery for degenerative lumbar canal stenosis.Spine J. 2008 Mar-Apr;8(2):380-4. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2007.01.010. Epub 2007 Mar 13. Spine J. 2008. PMID: 17433781
-
Erratum.Mult Scler. 2016 Oct;22(12):NP9-NP11. doi: 10.1177/1352458515585718. Epub 2015 Jun 3. Mult Scler. 2016. PMID: 26041800
-
The effect of weight management interventions that include a diet component on weight-related outcomes in pregnant and postpartum women: a systematic review protocol.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Jan;13(1):88-98. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-1812. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26447010
-
Effect of physical therapy on pain and function in patients with hip osteoarthritis: a randomized clinical trial.JAMA. 2014 May 21;311(19):1987-97. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.4591. JAMA. 2014. PMID: 24846036 Clinical Trial.
-
Novel Augmentation Strategies in Major Depression.Dan Med J. 2017 Apr;64(4):B5338. Dan Med J. 2017. PMID: 28385173 Review.
Cited by
-
Testing a novel multicomponent intervention to reduce meat consumption in young men.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 11;13(10):e0204590. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204590. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30307958 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Beyond Seasoning-The Role of Herbs and Spices in Rheumatic Diseases.Nutrients. 2023 Jun 20;15(12):2812. doi: 10.3390/nu15122812. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37375716 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nutritional aspects in chronic non-cancer pain: A systematic review.Front Nutr. 2022 Aug 8;9:931090. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.931090. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36003834 Free PMC article.
-
What makes a plant-based diet? a review of current concepts and proposal for a standardized plant-based dietary intervention checklist.Eur J Clin Nutr. 2022 Jun;76(6):789-800. doi: 10.1038/s41430-021-01023-z. Epub 2021 Oct 21. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2022. PMID: 34675405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Managing Psoriatic Arthritis With a Whole Food Plant-Based Diet: A Case Study.Am J Lifestyle Med. 2021 Feb 12;15(4):402-406. doi: 10.1177/1559827621993435. eCollection 2021 Jul-Aug. Am J Lifestyle Med. 2021. PMID: 34366737 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Craig W. J., Mangels A. R. Position of the American Dietetic Association: vegetarian diets. Journal of the American Dietetic Association. 2009;109(7):1266–1282. - PubMed
-
- Hänninen, Kaartinen K., Rauma A. L., et al. Antioxidants in vegan diet and rheumatic disorders. Toxicology. 2000;155(1–3):45–53. - PubMed
-
- Adam O., Beringer C., Kless T., et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of a low arachidonic acid diet and fish oil in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology International. 2003;23(1):27–36. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources