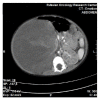
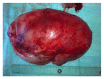
Anesthesia management of a 20-month-old patient with giant unilateral wilms tumor
- PMID: 25815216
- PMCID: PMC4357028
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/487219
Anesthesia management of a 20-month-old patient with giant unilateral wilms tumor
Abstract
Wilms tumour (WT) (or nephroblastoma) is one of the most common malignant kidney tumors in children. On subsequent stages clinically it is often characterized by abdominal hypertension syndrome, which, in turn, leads to development of respiratory insufficiency. Other symptoms comprise renal deficiency, hypertension, and abnormalities of hemostasis and hemogram. Treatment includes rounds of preoperative chemotherapy and subsequent surgery. We report a case of perioperative management for nephrectomy in 20-month-old patient with a giant unilateral WT. The complexity of anesthesia was determined by the size of tumor, increased intra-abdominal pressure, respiratory deficiency, and hypercoagulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Wilms tumor in a left pelvic kidney: A case report.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2020;66:115-117. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2019.11.041. Epub 2019 Nov 27. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 31837612 Free PMC article.
-
Complete necrosis induced by preoperative chemotherapy in Wilms tumor as an indicator of low risk: report of the international society of paediatric oncology (SIOP) nephroblastoma trial and study 9.Med Pediatr Oncol. 2000 Mar;34(3):183-90. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-911x(200003)34:3<183::aid-mpo4>3.0.co;2-o. Med Pediatr Oncol. 2000. PMID: 10696124 Clinical Trial.
-
Nephron-sparing procedures in 11 patients with Wilms' tumor.Pediatr Surg Int. 2003 Aug;19(6):457-62. doi: 10.1007/s00383-003-0957-x. Epub 2003 May 17. Pediatr Surg Int. 2003. PMID: 12756594
-
Anesthetic management of an infant undergoing radical nephrectomy for Wilms tumor: a case report.AANA J. 2008 Jun;76(3):199-201. AANA J. 2008. PMID: 18567324 Review.
-
Management of bilateral Wilms tumours.Pediatr Surg Int. 2017 Jul;33(7):737-745. doi: 10.1007/s00383-017-4091-6. Epub 2017 May 17. Pediatr Surg Int. 2017. PMID: 28516188 Review.
Cited by
-
Successful Imatinib Treatment of an Abdominal Compartment Syndrome due to Huge Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumour.Case Rep Oncol. 2019 Aug 13;12(2):644-649. doi: 10.1159/000502338. eCollection 2019 May-Aug. Case Rep Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31572153 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources