Descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty: intraoperative and postoperative imaging spectral-domain optical coherence tomography
- PMID: 25815221
- PMCID: PMC4357027
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/506251
Descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty: intraoperative and postoperative imaging spectral-domain optical coherence tomography
Abstract
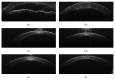
We describe a case report of using the same handheld spectral-domain anterior segment optical coherence tomography (ASOCT) for rapid intraoperative and postoperative imaging in a case of Descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty (DMEK). A 67-year-old woman, with Fuchs dystrophy and corneal decompensation, underwent DMEK with intraoperative ASOCT imaging using the handheld Envisu spectral domain ASOCT system (Bioptigen, Inc., Morrisville, NC, USA). We found that this easy-to-use portable system with handheld probe allowed for rapid imaging of the anterior segment during donor manipulation to visualize the orientation of the DMEK donor, as well as to confirm the initial adhesion of the DMEK donor. Moreover, the same system may be used for postoperative monitoring of graft adhesion, corneal thickness, and stromal remodeling in the clinic with very high-definition images.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

