Rate of early onset Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 25815299
- PMCID: PMC4356853
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2305-5839.2015.01.19
Rate of early onset Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Erratum in
-
Erratum to Rate of early onset Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Transl Med. 2016 May;4(9):E4. doi: 10.21037/atm.2016.05.21. Ann Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27275503 Free PMC article.
Abstract
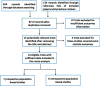
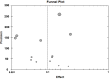
It is generally accepted that the population rate of early onset Alzheimer's disease (EOAD) in Alzheimer's disease (AD) is 1-2%. However, the true population based rate of EOAD has never been verified by a systematic review and meta-analysis. We used electronic searches of Cochrane Library, Embase, Medline and PubMed databases to identify published related studies. The systematic review and meta-analysis was then to be conducted to calculate a pooled rate of EOAD and make comparisons between studies and geographic distribution. A total of 13 papers were included in our systematic review and meta-analysis. The rate of EOAD, 5.5% [95% confidence interval (CI): 0.039-0.079, P<0.001], was generated after pooled analysis of all studies in random effect model. The pooled analysis of the rate in developed country was 5.9% (95% CI: 0.040-0.085, P<0.001). The pooled analysis of the rate in developing countries was 4.4% (95% CI: 0.028-0.066, P<0.001). Our study showed that the rate of EOAD in AD is 5.5%, not 1-2% as usually demonstrated. And our results indicated that the rate in developed countries was relative higher than in developing countries. Further trials with larger samples across more countries and more careful designed of experiments are required to confirm whether our findings are truly significant.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease (AD); Early onset Alzheimer’s disease (EOAD); meta-analysis; rate.
Figures


References
-
- Jiang T, Yu JT, Tan L. Novel disease-modifying therapies for Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis 2012;31:475-92. - PubMed
-
- Smits LL, Pijnenburg YA, Koedam EL, et al. Early onset Alzheimer's disease is associated with a distinct neuropsychological profile. J Alzheimers Dis 2012;30:101-8. - PubMed
-
- Querfurth HW, LaFerla FM. Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med 2010;362:329-44. - PubMed
-
- Jiang T, Yu JT, Tian Y, et al. Epidemiology and etiology of Alzheimer's disease: from genetic to non-genetic factors. Curr Alzheimer Res 2013;10:852-67. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
