Human RNASET2 derivatives as potential anti-angiogenic agents: actin binding sequence identification and characterization
- PMID: 25815360
- PMCID: PMC4341462
- DOI: 10.18632/oncoscience.100
Human RNASET2 derivatives as potential anti-angiogenic agents: actin binding sequence identification and characterization
Abstract
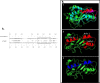
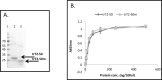
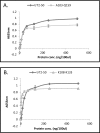
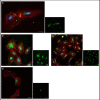
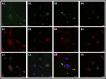
Human RNASET2 (hRNASET2) has been demonstrated to exert antiangiogenic and antitumorigenic effects independent of its ribonuclease capacity. We suggested that RNASET2 exerts its antiangiogenic and antitumorigenic activities via binding to actin and consequently inhibits cell motility. We focused herein on the identification of the actin binding site of hRNASET2 using defined sequences encountered within the whole hRNASET2 protein. For that purpose we designed 29 different hRNASET2-derived peptides. The 29 peptides were examined for their ability to bind immobilized actin. Two selected peptides-A103-Q159 consisting of 57 amino acids and peptide K108-K133 consisting of 26 amino acids were demonstrated to have the highest actin binding ability and concomitantly the most potent anti-angiogenic activity. Further analyses on the putative mechanisms associated with angiogenesis inhibition exerted by peptide K108-K133 involved its location during treatment within the HUVE cells. Peptide K108-K133 readily penetrates the cell membrane within 10 min of incubation. In addition, supplementation with angiogenin delays the entrance of peptide K108-K133 to the cell suggesting competition on the same cell internalization route. The peptide was demonstrated to co-localize with angiogenin, suggesting that both molecules bind analogous cellular epitopes, similar to our previously reported data for ACTIBIND and trT2-50.
Keywords: RNASET2; actin-binding; antiangiogenesis; peptides; ribonuclease.
Figures
References
-
- Folkman J. Biology of Endothelial Cells. Vol. 27. Boston, MA: Springer US; 1984. pp. 412–428.
-
- Sheetz MP, Felsenfeld D, Galbraith CG, Choquet D. Cell migration as a five-step cycle. Biochem Soc Symp. 1999;65:233–43. - PubMed
-
- Roiz L, Smirnoff P, Bar-Eli M, Schwartz B, Shoseyov O. ACTIBIND, an actin-binding fungal T2-RNase with antiangiogenic and anticarcinogenic characteristics. Cancer. 2006;106:2295–308. - PubMed
-
- Morales-Ruiz M, Fulton D, Sowa G, Languino LR, Fujio Y, Walsh K, Sessa WC. Vascular endothelial growth factor-stimulated actin reorganization and migration of endothelial cells is regulated via the serine/threonine kinase Akt. Circ Res. 2000;86:892–6. - PubMed
-
- Folkman J. Angiogenesis: an organizing principle for drug discovery? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2007;6:273–86. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

