Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia: prognosis and management
- PMID: 25815903
- PMCID: PMC4382666
- DOI: 10.1038/bcj.2015.28
Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia: prognosis and management
Erratum in
-
Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia: prognosis and management.Blood Cancer J. 2016 Feb 5;6(2):e391. doi: 10.1038/bcj.2015.42. Blood Cancer J. 2016. PMID: 26849012 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia (WM) is a B-cell lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma characterized by monoclonal immunoglobulin M protein in the serum and infiltration of bone marrow with lymphoplasmacytic cells. Asymptomatic patients can be observed without therapy. First-line therapy should consist of the monoclonal anti-CD20 antibody, rituximab, given typically in combination with other agents. We prefer dexamethasone, rituximab, cyclophosphamide (DRC) as initial therapy for most patients with symptomatic WM. Other reasonable options are bortezomib, rituximab, dexamethasone (BoRD) or bendamustine plus rituximab (BR). All of these regimens are associated with excellent response and tolerability. Initial therapy is usually administered for 6 months, followed by observation. Response to therapy is assessed using the standard response criteria developed by the International Working Group on Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia. Relapse is almost inevitable in WM but may occur years after initial therapy. In symptomatic patients relapsing more than 1-2 years after initial therapy, the original treatment can be repeated. For relapse occurring sooner, an alternative regimen is used. In select patients, high-dose chemotherapy followed by autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation may be an option at relapse. Options for therapy of relapsed WM besides regimens used in the front-line setting include ibrutinib, purine nucleoside analogs (cladribine, fludarabine), carfilzomib and immunomodulatory agents (thalidomide, lenalidomide).
Figures

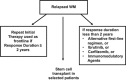
Similar articles
-
Waldenström macroglobulinemia: my way.Leuk Lymphoma. 2013 Mar;54(3):464-71. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2012.717173. Epub 2012 Aug 25. Leuk Lymphoma. 2013. PMID: 22860921 Review.
-
Waldenström macroglobulinemia: 2015 update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and management.Am J Hematol. 2015 Apr;90(4):346-54. doi: 10.1002/ajh.23922. Am J Hematol. 2015. PMID: 25808108
-
How I treat Waldenström macroglobulinemia.Blood. 2015 Aug 6;126(6):721-32. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-01-553974. Epub 2015 May 22. Blood. 2015. PMID: 26002963
-
Update on treatment recommendations from the Fourth International Workshop on Waldenstrom's Macroglobulinemia.J Clin Oncol. 2009 Jan 1;27(1):120-6. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.17.7865. Epub 2008 Dec 1. J Clin Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19047284 Review.
-
Waldenström macroglobulinemia: 2017 update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and management.Am J Hematol. 2017 Feb;92(2):209-217. doi: 10.1002/ajh.24557. Am J Hematol. 2017. PMID: 28094456
Cited by
-
Epidemiology, Staging, and Management of Multiple Myeloma.Med Sci (Basel). 2021 Jan 20;9(1):3. doi: 10.3390/medsci9010003. Med Sci (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33498356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Rare Case of Waldenstrom Macroglobulinemia of the Rectosigmoid Colon.ACG Case Rep J. 2021 Nov 29;8(11):e00689. doi: 10.14309/crj.0000000000000689. eCollection 2021 Nov. ACG Case Rep J. 2021. PMID: 34849377 Free PMC article.
-
MYD88 and CXCR4 Mutation Profiling in Lymphoplasmacytic Lymphoma/Waldenstrom's Macroglobulinaemia.Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2019 Jan;35(1):57-65. doi: 10.1007/s12288-018-0978-1. Epub 2018 Jul 2. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2019. PMID: 30828149 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence, prevalence, mortality, and causes of death in Waldenström macroglobulinemia: a nationwide, population-based cohort study.BMC Cancer. 2020 Jul 3;20(1):623. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07120-9. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32620091 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Diagnosis of Waldenström's Macroglobulinemia and Early Management: Perspectives from Clinical Practice.Blood Lymphat Cancer. 2022 Aug 18;12:107-117. doi: 10.2147/BLCTT.S259860. eCollection 2022. Blood Lymphat Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36003901 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gertz MA. Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia: 2013 update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and management. Am J Hematol. 2013;88:703–711. - PubMed
-
- Treon SP, Xu L, Yang G, Zhou Y, Liu X, Cao Y, et al. MYD88 L265P somatic mutation in Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:826–833. - PubMed
-
- Treon SP, Cao Y, Xu L, Yang G, Liu X, Hunter ZR. Somatic mutations in MYD88 and CXCR4 are determinants of clinical presentation and overall survival in Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia. Blood. 2014;123:2791–2796. - PubMed
-
- Castillo JJ, Olszewski AJ, Cronin AM, Hunter ZR, Treon SP. Survival trends in Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia: an analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results database. Blood. 2014;123:3999–4000. - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Sanz R, Montoto S, Torrequebrada A, de Coca AG, Petit J, Sureda A, et al. Waldenstrom macroglobulinaemia: presenting features and outcome in a series with 217 cases. Br J Haematol. 2001;115:575–582. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

