Hypothermia augments neuroprotective activity of mesenchymal stem cells for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- PMID: 25816095
- PMCID: PMC4376738
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120893
Hypothermia augments neuroprotective activity of mesenchymal stem cells for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
Abstract
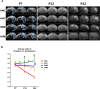
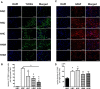
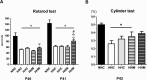
Though hypothermia is the only clinically available treatment for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE), it is not completely effective in severe cases. We hypothesized that combined treatment with hypothermia and transplantation of human umbilical cord blood (UCB)-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) would synergistically attenuate severe HIE compared to stand-alone therapy. To induce hypoxia-ischemia (HI), male Sprague-Dawley rats were subjected to 8% oxygen for 120 min after unilateral carotid artery ligation on postnatal day (P) 7. After confirmation of severe HIE involving >50% of the ipsilateral hemisphere volume as determined by diffusion-weighted brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) within 2 h after HI, intraventricular MSC transplantation (1 × 105 cells) and/or hypothermia with target temperature at 32°C for 24 h were administered 6 h after induction of HI. Follow-up brain MRI at P12 and P42, sensorimotor function tests at P40-42, evaluation of cytokines in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) at P42, and histologic analysis of peri-infarct tissues at P42 were performed. Severe HI resulted in progressively increased brain infarction over time as assessed by serial MRI, increased number of cells positive for terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase nick-end labeling, microgliosis and astrocytosis, increased CSF cytokine levels, and impaired function in behavioral tests such as rotarod and cylinder tests. All of the abnormalities observed in severe HIE showed greater improvement after combined treatment with hypothermia and MSC transplantation than with either therapy alone. Overall, these findings suggest that combined treatment with hypothermia and human UCB-derived MSC transplantation might be a novel therapeutic modality to improve the prognosis of severe HIE, an intractable disease that currently has no effective treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Johnston MV. Hypoxic and ischemic disorders of infants and children. Lecture for 38th meeting of Japanese Society of Child Neurology, Tokyo, Japan, July 1996. Brain Dev. 1997;19: 235–239. - PubMed
-
- Robertson C, Finer N. Term infants with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: outcome at 3.5 years. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1985;27: 473–484. - PubMed
-
- Jacobs S, Hunt R, Tarnow-Mordi W, Inder T, Davis P. Cooling for newborns with hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007: CD003311. - PubMed
-
- Shankaran S, Laptook A, Wright LL, Ehrenkranz RA, Donovan EF, Fanaroff AA, et al. Whole-Body Hypothermia for Neonatal Encephalopathy: Animal Observations as a Basis for a Randomized, Controlled Pilot Study in Term Infants. Pediatrics. 2002;110: 377–385. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

