Pharmacokinetics and tolerability of inhaled umeclidinium and vilanterol alone and in combination in healthy Chinese subjects: a randomized, open-label, crossover trial
- PMID: 25816315
- PMCID: PMC4376748
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121264
Pharmacokinetics and tolerability of inhaled umeclidinium and vilanterol alone and in combination in healthy Chinese subjects: a randomized, open-label, crossover trial
Abstract
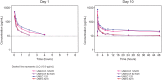
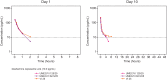
Inhaled umeclidinium (UMEC) and the combination of inhaled UMEC with vilanterol (UMEC/VI) are approved maintenance treatments for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in the US and EU. This was a randomized, open-label, three-period crossover, single- and repeat-dose study to assess the pharmacokinetics (PK), safety, and tolerability of inhaled UMEC/VI 62.5/25 μg (delivering 55/22 μg) and UMEC/VI 125/25 μg (delivering 113/22 μg) compared with their monotherapy components (UMEC 62.5 μg, UMEC 125 μg and, VI 25 μg [delivering 55, 113, and 22 μg, respectively]) in healthy Chinese subjects (n=20). UMEC and VI were rapidly absorbed following single and repeat dosing (time to maximum plasma concentration [tmax]: UMEC = 5 min; VI = 5 min). The median tlast was 2–4 h for UMEC and 1–2 h for VI following single doses of UMEC/VI and UMEC monotherapy (both doses). UMEC reached steady-state prior to Day 10; steady-state for VI could not be assessed. UMEC accumulation following repeat dosing was 11–34% based on Cmax and 19–59% based on area under the concentration-time curve from time zero to 2 h (AUC(0-2)). VI accumulation following repeat dosing was 25–66% based on Cmax and 17–43% based on AUC(0-2). The evidence was not sufficient to suggest that systemic exposure was substantially different between UMEC/VI combination therapy and the constituent monotherapies following single or repeat dosing. Following both single- and repeat-dose administration, the inter-subject coefficient of variation for all UMEC PK parameter estimates ranged from 12% to 165% for all treatments, indicating a wide range of variability in inhaled PK parameters. Twelve subjects experienced ≥1 adverse event (AE). Six subjects experienced ≥1 treatment-related AE; the most commonly reported treatment-related AE was chest discomfort (n=3 [15%]). No clinically important changes in vital signs or electrocardiogram parameters were reported. These data suggest that single- and repeat-dose administration of UMEC/VI combination therapy in healthy Chinese subjects did not result in substantial differences in systemic exposure compared with UMEC and VI as monotherapies.
Trial registration: Clinicaltrials.gov NCT01899638 NCT01899638.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Celli BR, MacNee W. Standards for the diagnosis and treatment of patients with COPD: a summary of the ATS/ERS position paper. Eur Respir J. 2004;23:932–946. - PubMed
-
- NICE. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in adults in primary and secondary care (partial update). 2010. Available: http://guidance.nice.org.uk/CG101/NICEGuidance/pdf/English. Accessed 1 October 2014.
-
- Barnes PJ. The role of anticholinergics in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Med. 2004;117(Suppl 12A):24S–32S. - PubMed
-
- GlaxoSmithKline. Anoro Ellipta. Summary of product characteristics. 2014. Available: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Product_Info.... Accessed 1 October 2014.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

