Pharmacologic inhibition of the Menin-MLL interaction blocks progression of MLL leukemia in vivo
- PMID: 25817203
- PMCID: PMC4415852
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2015.02.016
Pharmacologic inhibition of the Menin-MLL interaction blocks progression of MLL leukemia in vivo
Abstract
Chromosomal translocations affecting mixed lineage leukemia gene (MLL) result in acute leukemias resistant to therapy. The leukemogenic activity of MLL fusion proteins is dependent on their interaction with menin, providing basis for therapeutic intervention. Here we report the development of highly potent and orally bioavailable small-molecule inhibitors of the menin-MLL interaction, MI-463 and MI-503, and show their profound effects in MLL leukemia cells and substantial survival benefit in mouse models of MLL leukemia. Finally, we demonstrate the efficacy of these compounds in primary samples derived from MLL leukemia patients. Overall, we demonstrate that pharmacologic inhibition of the menin-MLL interaction represents an effective treatment for MLL leukemias in vivo and provide advanced molecular scaffold for clinical lead identification.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant conflict of interest.
Figures

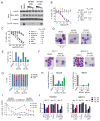
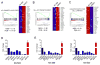
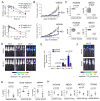
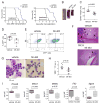
Comment in
-
Designed to kill: novel menin-MLL inhibitors target MLL-rearranged leukemia.Cancer Cell. 2015 Apr 13;27(4):431-3. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2015.03.012. Cancer Cell. 2015. PMID: 25873167
-
Therapy: It's raining menin.Nat Rev Cancer. 2015 May;15(5):256-7. doi: 10.1038/nrc3951. Epub 2015 Apr 16. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25877330 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

